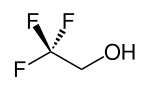
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanol
Trifluoroethanol is produced industrially by hydrogenation or the hydride reduction of derivatives of trifluoroacetic acid, such as the esters or acyl chloride.
[1] TFE can also be prepared by hydrogenolysis of compounds of generic formula CF3−CHOH−OR (where R is hydrogen or an alkyl group containing from one to eight carbon atoms), in the presence of a palladium containing catalyst deposited on activated charcoal.
[5] TFE forms complexes with Lewis bases such as THF or pyridine through hydrogen bonding, yielding 1:1 adducts.
[6] It is classified as a hard Lewis acid and its acceptor properties are discussed in the ECW model yielding EA = 2.07 and CA = 1.06.
[1] Trifluoroethanol is classified as toxic to blood, the reproductive system, bladder, brain, upper respiratory tract and eyes.