2013 Saravan earthquake
The shock struck a mountainous area between the cities of Saravan and Khash in Sistan and Baluchestan province, Iran, close to the border with Pakistan,[2][3][4][5] with a duration of about 25 seconds.
[11] Although the earthquake was much stronger than previous ones in the area, the depth and the terrain/population density above the focus, as well as predominating building construction being relatively light materials such as mud and wood, meant that there were relatively few casualties in Iran, although the number of casualties was higher in the neighbouring state of Pakistan, with at least 34 reported deaths.
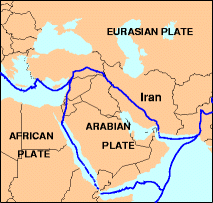
To the northwest, continental crust portions of the Arabian and Eurasian plates are colliding, resulting in compressive faulting.
The specific area of the fault that lies below the Sistan and Baluchestan province is referred to as the Makran region.
In the entire 20th century Pakistan and Iran experienced a combined total of twenty-six earthquakes.
This system is monitored by the Japanese Meteorological Agency The JMA sends out the warnings through the television, mobile devices, the internet, and the radio as soon as an earthquake is detected.
One study conducted in California, United States suggests there may be a new way to more precisely presage earthquakes.
[15] These principles include ensuring respect for all humans, making no discrimination as to nationality, religious beliefs, or political opinion, and remaining neutral in times of controversy.
[15] These four goals are: reducing the deaths, injuries, and impact caused by the disaster; decreasing the amount of death and illnesses caused by diseases and public health emergencies; increasing its ability to address the urgent situations; and promote respect for human dignity while reducing intolerance and discrimination.
[15] On 9 April 2013, the IFRC deployed seventy-five rescue teams to northwestern Iran following a 6.3 magnitude earthquake.
[16] A week later a 7.8 magnitude earthquake struck southeastern Iran, the IFRC dispatched air assessment teams in addition to forty ambulances.
[18] The earthquake, measuring 7.7 on the moment magnitude scale, was not only felt in this southeastern area of Iran and Pakistan but also as far away as India's capital city of Delhi.
[19] The lack of actual structures contributed to the minimal damage which occurred due to this earthquake.