American Astronomical Society 215th meeting
It is one of the largest astronomy meetings ever to take place as 3,500 astronomers and researchers were expected to attend and give more than 2,200 scientific presentations.
An infrared snapshot of a region in the constellation Carina, near the Milky Way was taken shortly after the survey telescope ejected its cover.
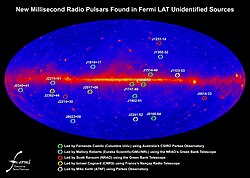
Unknown high-energy sources detected by NASA's Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope revealed the existence and location of the pulsars.
This is an accelerated pace for discovering such objects, which could be used as a "galactic GPS" to detect gravitational waves passing near Earth.
The differences in temperature counteract the natural gravitational pull of the sun (or proto-sun), at a crucial time during planet formation.
The discovery of HD156668b, a super-Earth class exoplanet, was announced on January 7, 2010, at the 215th meeting American Astronomical Society (AAS), in Washington DC.
With the twin telescopes functioning as a single observatory, by means of interferometry, it was determined that HD156668b is only four times larger than the Earth, and the second smallest exoplanet yet found.
For example, the Kepler mission, is part of the intense popular interest surrounding the discovery of hundreds of planets orbiting other stars.
Kepler telescope, however has a more specific mission - to discover hundreds of terrestrial planets which are defined as exoplanets that are one half to twice the size of the Earth.
The first 32 pair by the DEEP2 Galaxy Redshift Survey conducted with the Keck II Telescope on Hawaii's Mauna Kea.
[10][11] In a globular cluster 65 million light years from Earth evidence is accumulating that a black hole, one thousand times more massive than the sun, has caused the destruction of a white dwarf star.
[12][13][14] A mix of detected natural elements seems to indicate the actual source of the X-ray emissions are debris from the white dwarf.
The spectrum reveals emission from oxygen and nitrogen but no hydrogen, a rare set of signals from within globular clusters.
The physical conditions deduced from the spectra suggest that the gas is orbiting a black hole of at least 1,000 solar masses.
[14] To explain these observations, researchers suggest that a white dwarf star strayed too close to an intermediate-mass black hole and was ripped apart by tidal forces.
Astronomers have long suspected globular clusters contained intermediate-mass black holes, but there has been no conclusive evidence of their existence there to date.
The research is the first time scientists have measured the three-dimensional shape of a dark matter halo [citation needed].