2nd millennium BC
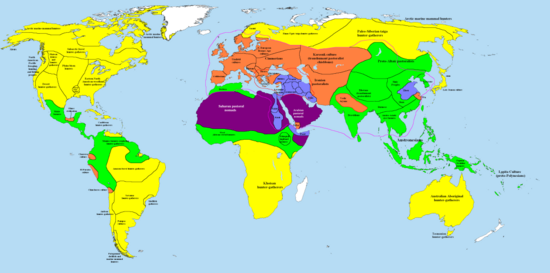
The Ancient Near Eastern cultures are well within the historical era: The first half of the millennium is dominated by the Middle Kingdom of Egypt and Babylonia.
The Pharaohs of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt and their contemporary Kings of Babylon, of Amorite origin, brought governance that was largely popular and approved of among their subjects, and favoured elegant art and architecture.
Combined with a weak economy and difficulty in maintaining order, this was a fragile situation that crumbled under the pressure of external forces they could not oppose.
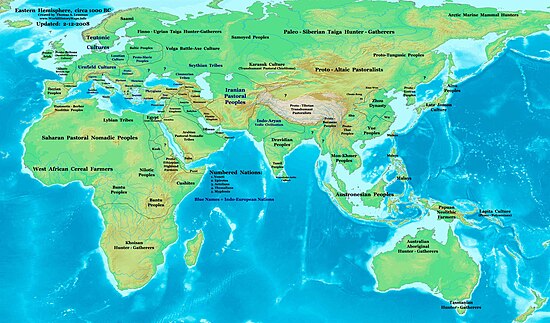
About a century before the middle of the millennium, bands of Indo-European invaders came from the Central Asian plains and swept through Western Asia and Northeast Africa.
They were riding fast two-wheeled chariots powered by horses, a system of weaponry developed earlier in the context of plains warfare.
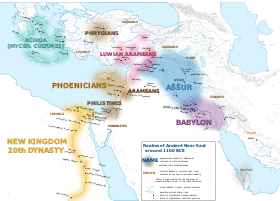
Though during most of the second half of the 2nd millennium BC several regional powers competed relentlessly for hegemony, many developments occurred: there was new emphasis on grandiose architecture, new clothing fashions, vivid diplomatic correspondence on clay tablets, renewed economic exchanges, and the New Kingdom of Egypt played the role of the main superpower.
Among the great states of the time, only Babylon refrained from taking part in battles, mainly due to its new position as the world's religious and intellectual capital.
The Bronze Age civilization at its final period of time, displayed all its characteristic social traits: low level of urbanization, small cities centered on temples or royal palaces, strict separation of classes between an illiterate mass of peasants and craftsmen, and a powerful military elite, knowledge of writing and education reserved to a tiny minority of scribes, and pronounced aristocratic life.