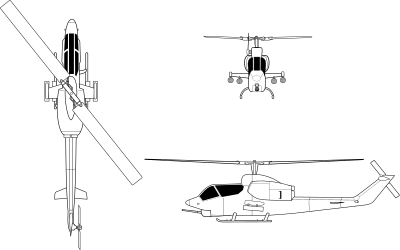
Bell AH-1 SuperCobra
The Bell AH-1 SuperCobra is a twin-engined attack helicopter that was developed on behalf of, and primarily operated by, the United States Marine Corps (USMC).
The USMC had quickly taken an interest in the type, but sought a twin-engined arrangement for greater operational safety at sea, along with more capable armaments.
The USMC promptly sought greater payload capacity than that provided by the original Sea Cobra; thus the AH-1T, equipped with the dynamic systems of the Model 309 and a lengthened fuselage, was produced by Bell during the 1970s.
The Sea Cobra was involved in multiple major operations during the latter half of the twentieth century, such as during the United States invasion of Grenada in 1983.
The Cobra shared the proven transmission, rotor system, and the Lycoming T53 turboshaft engine of the prolific UH-1 "Huey" utility helicopter.
[2] The U.S. Marine Corps became particularly interested in the AH-1G Cobra, but expressed its preference for a twin-engined configuration that would provide improved safety in over-water operations.
Initially, the Department of Defense had balked at providing the Marines with a twin-engine version of the Cobra in the belief that commonality with the Army's AH-1Gs outweighed the advantages of a different engine arrangement.
[11] During the late 1990s, Bell was negotiating to acquire the Romanian state-managed helicopter manufacturer IAR Brașov with the intention of establishing an overseas production line for the AH-1W for multiple export customers.
[12] In May 1997, the company signed an agreement with the Romanian State Ownership Fund to buy the government's 70 percent stake in IAR Brașov.
[13] However, during November 1999, following protracted negotiations, Bell announced that it had abandoned its acquisition efforts, and thus the overseas production initiative, after the Romanian government had allegedly ceased responding to its proposals.
They were typically used to perform close air support and helicopter escort missions; a total of two AH-1Ts were shot down and three crew members killed.
[4] That same year, Marine AH-1s were also deployed off the coast of Beirut, Lebanon, amid the Lebanese civil war in support of the Multinational Peacekeeping Force.
[20] In this theatre, the AH-1s were typically armed with Sidewinder missiles and guns, which were intended to be used as an emergency air defense measure to counter the threat of light civil aircraft being piloted by suicide bombers.
The AH-1W units were credited with destroying 97 tanks, 104 armored personnel carriers and vehicles, and two anti-aircraft artillery sites during the 100-hour ground campaign.
USMC Cobras were used in U.S. military interventions in the former Yugoslavia in the 1990s; specifically, two AH-1Ws assisted in the rescue of USAF Captain Scott O'Grady, after his F-16 was shot down by a SAM in June 1995.
[27] During the opening phase of the 2003 invasion of Iraq, SuperCobras were deployed on the front lines, often flying in hunter-killer teams with Bell UH-1 Iroquois utility helicopters and other coalition aircraft.
[31] In the later stages of the operation, AH-1Ws flew combat missions from the deck of USS San Antonio after that ship replaced Wasp in October 2016.
[36] Iranian AH-1Js (particularly the TOW-capable ones) were "exceptionally effective" in anti-armor warfare, inflicting heavy losses on Iraqi armored and vehicle formations.
[37][38] Due to the post-Revolution weapons sanctions, Iranians had to make do with what was at hand: they equipped the AH-1Js with AGM-65 Maverick missiles and used them with some success in several operations.
[39] Ali Akbar Shiroodi and Ahmad Keshvari were two distinguished Iranian Cobra pilots during Iran-Iraq War and are considered wartime heroes in Iran.
Into the twenty-first century, Iranian AH-1Js remain in service with the Islamic Republic of Iran Army Aviation and have undergone indigenous upgrade programs.
[49] The sale was politically controversial in the United States; in April 1996, the purchase of ten additional AH-1Ws by Turkey was blocked by the Clinton administration.
[55][56] On 13 May 2016, PKK militants shot down a Turkish Army AH-1W SuperCobra using a 9K38 Igla (SA-18 Grouse) MANPADS; in the published video, the missile severed the tail section from the rest of the helicopter, causing it to spin, fragment in midair and crash, killing the two pilots on board.
[60] Being already appropriately suited to maritime operations, the AH-1Ws are to be used on board the TCG Anadolu amphibious assault ship; as such, the type has been speculated to have displaced a planned navalised version of the indigenously built TAI/AgustaWestland T129 ATAK attack helicopter.