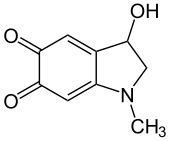
Adrenochrome
[1] The oxidation reaction that converts adrenaline into adrenochrome occurs both in vivo and in vitro.
[4] Several small-scale studies (involving 15 or fewer test subjects) conducted in the 1950s and 1960s reported that adrenochrome triggered psychotic reactions such as thought disorder and derealization.
[5] In 1954, researchers Abram Hoffer and Humphry Osmond claimed that adrenochrome is a neurotoxic, psychotomimetic substance and may play a role in schizophrenia and other mental illnesses.
[10] Multiple additional studies in the United States,[11] Canada,[12] and Australia[13] similarly failed to find benefits of megavitamin therapy to treat schizophrenia.
[citation needed] In the early 2000s, interest was renewed by the discovery that adrenochrome may be produced normally as an intermediate in the formation of neuromelanin.