Artery
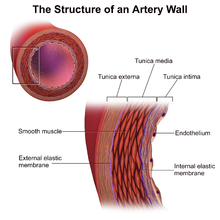
The externa, alternatively known as the tunica adventitia, is composed of collagen fibers and elastic tissue—with the largest arteries containing vasa vasorum, small blood vessels that supply the walls of large blood vessels.
They are the primary "adjustable nozzles" in the blood system, across which the greatest pressure drop occurs.
Systemic arteries deliver blood to the arterioles, and then to the capillaries, where nutrients and gasses are exchanged.
This smooth muscle contraction is primarily influenced by activity of the sympathetic vasomotor nerves innervating the arterioles.
In humans, it receives blood directly from the left ventricle of the heart via the aortic valve.
The microvessels have a width of a single cell in diameter to aid in the fast and easy diffusion of gasses, sugars and nutrients to surrounding tissues.
These small diameters of the capillaries provide a relatively large surface area for the exchange of gasses and nutrients.
Systemic arterial pressures are generated by the forceful contractions of the heart's left ventricle.
To withstand and adapt to the pressures within, arteries are surrounded by varying thicknesses of smooth muscle which have extensive elastic and inelastic connective tissues.
The pulse pressure, being the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure, is determined primarily by the amount of blood ejected by each heart beat, stroke volume, versus the volume and elasticity of the major arteries.
[11] Over time, factors such as elevated arterial blood sugar (particularly as seen in diabetes mellitus), lipoprotein, cholesterol, high blood pressure, stress and smoking, are all implicated in damaging both the endothelium and walls of the arteries, resulting in atherosclerosis.
This is caused by an atheroma or plaque in the artery wall and is a build-up of cell debris, that contain lipids, (cholesterol and fatty acids), calcium[12][13] and a variable amount of fibrous connective tissue.
Accidental intra-arterial injection either iatrogenically or through recreational drug use can cause symptoms such as intense pain, paresthesia and necrosis.
In medieval times, it was supposed that arteries carried a fluid, called "spiritual blood" or "vital spirits", considered to be different from the contents of the veins.
[19] William Harvey described and popularized the modern concept of the circulatory system and the roles of arteries and veins in the 17th century.
Alexis Carrel at the beginning of the 20th century first described the technique for vascular suturing and anastomosis and successfully performed many organ transplantations in animals; he thus actually opened the way to modern vascular surgery that was previously limited to vessels' permanent ligation.