Asynchronous connection-oriented logical transport
Certain combinations are intended for use in different application types which have particular requirements regarding issues such as topology, timing, reliability and radio channel use.
Amongst these parameters are connection interval, supervision timeout, peripheral latency and channel map.
At the start of each connection event, the radio channel to be used is selected using a procedure known as adaptive frequency hopping.
Central and Peripheral may then proceed to exchange a further implementation-defined number of packets during the remainder of the connection event.
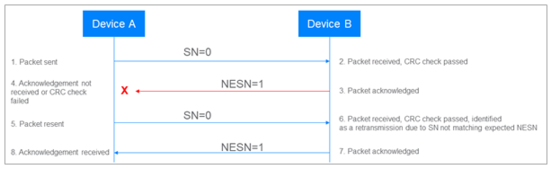
Link layer data packets contain three important fields which contribute to communication being reliable.
From this point on, at each packet exchange that takes place, if all is well, the value of the SN field as set by Device A, will alternate between zero and one.
Each device in the connection will then switch to the selected channel and over time and a series of connection events, communication will take place using a frequently changing series of different channels, distributed across the 2.4 GHz band, thereby significantly reducing the probability of collisions occurring.
In this way, adaptive frequency hopping dynamically adjusts the channels used for active communication according to the prevailing RF conditions in the environment.
This ratio of used to skipped connection events is determined by the subrate factor parameter and in this example it is set to 5.
Subrated connections have a number of special Link Layer control procedures defined for use with them.
This capability has particular applicability in some LE Audio scenarios such as those involving hearing aids and smartphones.
The Bluetooth Core Specification Version 5.3 Feature Enhancements paper has a substantial chapter dedicated to the subject of subrated connections and is recommended as a source of further information.
When a BR/EDR device joins a piconet, a default ACL logical transport automatically created.
BR/EDR ACL connections make use of time slots defined by the underlying physical channel.
Central and Peripheral devices alternately transmit and receive during a subset of these time slots, allocated by the implementation.
Bluetooth Enhanced Data Rate (EDR) defines a further six packet types named 2-DH1, 3-DH1, 2-DH3, 3-DH3, 2-DH5 and 3-DH5.
1-bit header fields ARQN and SEQN are used to allow positive or negative acknowledgements to be made and to verify that the order of packets received is as it should be.
The Link Manager Protocol (LMP) defines a series of PDU types which allow the control of and negotiation over details of the BR/EDR ACL logical transport to be carried out.