Babylonia
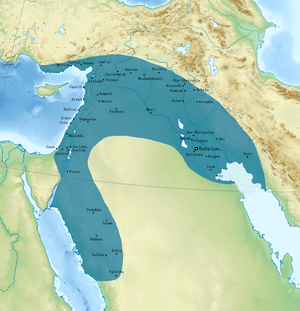
Babylonia (/ˌbæbɪˈloʊniə/; Akkadian: 𒆳𒆍𒀭𒊏𒆠, māt Akkadī) was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran).
Traditionally, the major religious center of all Mesopotamia was the city of Nippur where the god Enlil was supreme, and it would remain so until replaced by Babylon during the reign of Hammurabi in the mid-18th century BC.
The empire eventually disintegrated due to economic decline, climate change, and civil war, followed by attacks by the language isolate speaking Gutians from the Zagros Mountains to the northeast.
Under these kings, Babylonia remained a small nation which controlled very little territory, and was overshadowed by neighbouring kingdoms that were both older, larger, and more powerful, such as; Isin, Larsa, Assyria to the north and Elam to the east in ancient Iran.
He then systematically conquered southern Mesopotamia, including the cities of Isin, Larsa, Eshnunna, Kish, Lagash, Nippur, Borsippa, Ur, Uruk, Umma, Adab, Sippar, Rapiqum, and Eridu.
After a protracted struggle over decades with the powerful Assyrian kings Shamshi-Adad I and Ishme-Dagan I, Hammurabi forced their successor Mut-Ashkur to pay tribute to Babylon c. 1751 BC, giving Babylonia control over Assyria's centuries-old Hattian and Hurrian colonies in Anatolia.
Hammurabi transferred this dominance to Babylon, making Marduk supreme in the pantheon of southern Mesopotamia (with the god Ashur, and to some degree Ishtar, remaining the long-dominant deity in northern Mesopotamian Assyria).
Hammurabi turned what had previously been a minor administrative town into a large, powerful and influential city, extended its rule over the entirety of southern Mesopotamia, and erected a number of buildings.
After six years of civil war in Assyria, a native king named Adasi seized power c. 1735 BC, and went on to appropriate former Babylonian and Amorite territory in central Mesopotamia, as did his successor Bel-bani.
Babylon continued to be the capital of the kingdom and one of the holy cities of western Asia, where the priests of the ancient Mesopotamian religion were all-powerful, and the only place where the right to inheritance of the short lived old Babylonian empire could be conferred.
From there Agum III extended farther south still, invading what was many centuries later to be called the Arabian Peninsula or Arabia, and conquering the pre-Arab state of Dilmun (in modern Bahrain).
He describes having "annihilated their extensive forces", then constructed fortresses in a mountain region called Ḫiḫi, in the desert to the west (modern Syria) as security outposts, and "he dug wells and settled people on fertile lands, to strengthen the guard".
However, East Semitic-speaking Babylonia soon began to suffer further repeated incursions from West Semitic nomadic peoples migrating from the Levant during the Bronze Age collapse, and during the 11th century BC large swathes of the Babylonian countryside was appropriated and occupied by these newly arrived Arameans and Suteans.
Adad-nirari II twice attacked and defeated Shamash-mudammiq of Babylonia, annexing a large area of land north of the Diyala River and the towns of Hīt and Zanqu in mid Mesopotamia.
It was during the late 850s BC, in the annals of Shalmaneser III, that the Chaldeans and Arabs dwelling in some northern regions of the Arabian Peninsula are first mentioned in the pages of written recorded history.
Upon the death of Shalmaneser II, Baba-aha-iddina was reduced to vassalage by the Assyrian queen Shammuramat (known as Semiramis to the Persians, Armenians and Greeks), acting as regent to his successor Adad-nirari III who was merely a boy.
Elam was destroyed once and for all, and the Babylonians, Persians, Chaldeans, Arabs, Medes, Elamites, Arameans, Suteans and Canaanites were violently subjugated, with Assyrian troops exacting savage revenge on the rebelling peoples.
It was during the reign of Sin-shar-ishkun that Assyria's vast empire began to unravel, and many of its former subject peoples ceased to pay tribute, most significantly for the Assyrians; the Babylonians, Chaldeans, Medes, Persians, Scythians, Arameans and Cimmerians.
The stalemate ended in 615 BC, when Nabopolassar entered the Babylonians and Chaldeans into alliance with Cyaxares, an erstwhile vassal of Assyria, and king of the Iranian peoples; the Medes, Persians, Sagartians and Parthians.
The fighting continued, as the Assyrian king held out against the alliance until 607 BC, when he was eventually ejected by the Medes, Babylonians, Scythians and their allies, and prevented in an attempt to regain the city the same year.
However, an attempt to take Egypt itself as his Assyrian predecessors had succeeded in doing failed, mainly due to a series of rebellions from the Israelites of Judah and the former kingdom of Ephraim, the Phoenicians of Caanan and the Arameans of the Levant.
He excited a strong feeling against himself by attempting to centralize the polytheistic religion of Babylonia in the temple of Marduk at Babylon, and while he had thus alienated the local priesthoods, the military party also despised him on account of his antiquarian tastes.
He seemed to have left the defense of his kingdom to his son Belshazzar (a capable soldier but poor diplomat who alienated the political elite), occupying himself with the more congenial work of excavating the foundation records of the temples and determining the dates of their builders.
[36] Cyrus now claimed to be the legitimate successor of the ancient Babylonian kings and the avenger of Bel-Marduk, who was assumed to be wrathful at the impiety of Nabonidus in removing the images of the local gods from their ancestral shrines to his capital Babylon.
[36] The Chaldean tribe had lost control of Babylonia decades before the end of the era that sometimes bears their name, and they appear to have blended into the general populace of Babylonia even before this (for example, Nabopolassar, Nebuchadnezzar II and their successors always referred to themselves as Shar Akkad and never as Shar Kaldu on inscriptions), and during the Persian Achaemenid Empire the term Chaldean ceased to refer to a race of people, and instead specifically to a social class of priests educated in classical Babylonian literature, particularly Astronomy and Astrology.
It was only when Darius I acquired the Persian throne and ruled it as a representative of the Zoroastrian religion that the old tradition was broken and the claim of Babylon to confer legitimacy on the rulers of West Asia ceased to be acknowledged.
[citation needed] It has long been maintained that the foundation of Seleucia diverted the population to the new capital of Lower Mesopotamia and that the ruins of the old city became a quarry for the builders of the new seat of government,[36] but the recent publication of the Babylonian Chronicles has shown that urban life was still very much the same well into the Parthian Empire (150 BC to 226 AD).
In Babylonia, an abundance of clay, and lack of stone, led to greater use of mudbrick; Babylonian, Sumerian and Assyrian temples were massive structures of crude brick which were supported by buttresses, the rain being carried off by drains.
The MUL.APIN, contains catalogues of stars and constellations as well as schemes for predicting heliacal risings and the settings of the planets, lengths of daylight measured by a water clock, gnomon, shadows, and intercalations.
According to the assyriologist Marc Van de Mieroop, Babylonian philosophy was a highly developed system of thought with a unique approach to knowledge and a focus on writing, lexicography, divination, and law.