London Borough of Barking and Dagenham
The area covered by Mayesbrook Park in the Borough was once part of the historic Manor of Jenkins, seat of the Fanshawe family.
See List of areas of London The borough's major districts include Barking, Becontree and Dagenham.
It borders five other London boroughs: Newham, Redbridge, Havering, and Greenwich and Bexley to the south of the Thames.
Much of the borough is within the London Riverside area of the Thames Gateway zone and is the site of considerable house building and other development, such as Beam Park.
[15] In 1801, the civil parishes that form the modern borough had a total population of 1,937; and the area was characterised by farming, woodland and the fishing fleet at Barking.
This last industry employed 1,370 men and boys by 1850, but by the end of the century had ceased to exist; replaced by train deliveries of fresh fish from the East Coast ports.
[17] The population rose slowly through the 19th century, as the district became built up; and new industries developed around Barking.
The population rose dramatically between 1921 and 1931, when the London County Council developed the Becontree Estate.
[18] In 1931, the Ford Motor Company relocated to a 500 acres (2.0 km2) site at Dagenham, and in 1932 the District line was extended to Upminster; bringing further development to the area.
After World War II, further public housing projects were built to rehouse the many Londoners made homeless in the Blitz.
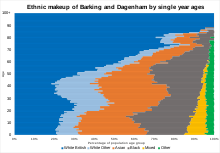
Barking and Dagenham has been strongly influenced by immigration, with the white British population having dropped 30.6% from 2001 to 2011 - the second largest decrease in the country, behind neighbouring Newham.
The borough also had the largest proportion of school-age (5-19) population of all the local authorities in England and Wales, 21.4%, at the 2011 census.
It also includes a library with free public internet access, the council's first One Stop Shop, conference and meeting space, a gallery and a café.
CU London, a Higher Education institute owned and governed by Coventry University, started offering courses to students in September 2017.
[31] Situated in the former Dagenham Civic Centre, they offer a range of subjects across Foundation, HNC, HND and degree level.
In March 2011, the main forms of transport that residents used to travel to work were: driving a car or van, 22.5% of all residents aged 16–74; underground, metro, light rail, tram, 7.5%; bus, minibus or coach, 7.5%; train, 7.3%; on foot, 3.7%; passenger in a car or van, 1.7%; work mainly at or from home, 1.3%.
TfL plans to extend the cycle network to Barking Riverside; the first consultations about this closed in winter 2019.
To the west, the A12 carries traffic through Newbury Park towards the North Circular, Stratford and Central London.
Other A-roads cross the Borough, including the A118, A123, A124, A1083, A1112, and A1306, although these roads are smaller and generally carry less traffic.
The support units that are operated here will cover a large selection of station grounds and areas.
[40] The coat of arms of the borough displays the Curfew tower of Barking Abbey in its crest.