Batty Langley
An eccentric landscape designer, he gave four of his sons the names Hiram, Euclid, Vitruvius and Archimedes.
He started worked as a gardener, inheriting some of his father's clients in Twickenham, then a village of suburban villas within easy reach of London by a pleasant water journey on the Thames.
Inspired by Switzer's Ichnographia Rustica of 1718, Langley advocated more irregular, informal gardens, with rococo "arti-natural" landscaping.
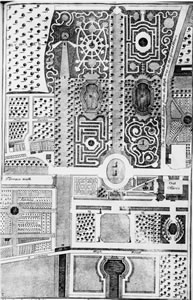
For the Palladian house built at Twickenham by James Johnston in 1710 (later Orleans House, demolished 1926), Langley, probably on his own endeavour, prepared and published a garden plan, which offered an encyclopaedia of the garden features that were swiftly becoming obsolete by the time the plan was published in Langley's A Sure Method of Improving Estates (1728): here are several mazes, a "wilderness" with many tortuous path-turnings, garden rooms or cabinets de verdure cut into dense woodland, formal stretches of garden canal and formally shaped basins of water, some with central fountains, and a central allée of trees leading to an exedra.
His New Principles of Gardening (1728) included designs for mazes, a feature he could never quite leave behind, with 28 plates engraved by his brother Thomas.
He is best known for one of his confident self-promotions, Ancient Architecture, Restored, and Improved published in 1742 and reissued in 1747 as Gothic Architecture, improved by Rules and Proportions, a bit of cockscombry that thoroughly irritated Horace Walpole, whose Gothick villa at Twickenham, Strawberry Hill, gave impetus to the stirrings of the Gothic Revival: All that his books achieved, has been to teach carpenters to massacre that venerable species, and to give occasion to those who know nothing of the matter, and who mistake his clumsy efforts for real imitations, to censure the productions of our ancestors, whose bold and beautiful fabrics Sir Christopher Wren viewed and reviewed with astonishment, and never mentioned without esteem.
He provided inspiration for elements of buildings from Great Fulford and Hartland Abbey in Devon, to Speedwell Castle in Brewood in Staffordshire, and Tissington Hall in Derbyshire, and the Gothic temple at Bramham Park in Yorkshire, and gates at Castletown House in County Kildare.