Binary code
A binary code represents text, computer processor instructions, or any other data using a two-symbol system.
[1][2]In Leibniz's view, binary numbers represented a fundamental form of creation, reflecting the simplicity and unity of the divine.
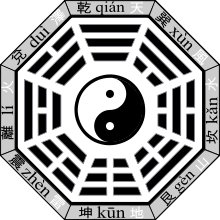
[2] Leibniz explained in his work that he encountered the I Ching by Fu Xi[2] that dates from the 9th century BC in China,[3] through French Jesuit Joachim Bouvet and noted with fascination how its hexagrams correspond to the binary numbers from 0 to 111111, and concluded that this mapping was evidence of major Chinese accomplishments in the sort of philosophical visual binary mathematics he admired.
[7] The Indian scholar Pingala (around 5th–2nd centuries BC) developed a binary system for describing prosody in his Chandashutram.
[10] In the 11th century, scholar and philosopher Shao Yong developed a method for arranging the hexagrams which corresponds, albeit unintentionally, to the sequence 0 to 63, as represented in binary, with yin as 0, yang as 1 and the least significant bit on top.
[11] In 1605 Francis Bacon discussed a system whereby letters of the alphabet could be reduced to sequences of binary digits, which could then be encoded as scarcely visible variations in the font in any random text.
[13] This system was not put into use until a graduate student from Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Claude Shannon, noticed that the Boolean algebra he learned was similar to an electric circuit.
Shannon's thesis became a starting point for the use of the binary code in practical applications such as computers, electric circuits, and more.
The different combinations of raised and flattened dots are capable of representing all letters, numbers, and punctuation signs.
The Ifá/Ifé system of divination in African religions, such as of Yoruba, Igbo, and Ewe, consists of an elaborate traditional ceremony producing 256 oracles made up by 16 symbols with 256 = 16 x 16.
Then, divination nuts or a pair of chains are used to produce random binary numbers,[16] which are drawn with sandy material on an "Opun" figured wooden tray representing the totality of fate.
The remaining six values are illegal and may cause either a machine exception or unspecified behavior, depending on the computer implementation of BCD arithmetic.