Biomedical engineering
BME is also traditionally logical sciences to advance health care treatment, including diagnosis, monitoring, and therapy.
[1][2] Also included under the scope of a biomedical engineer is the management of current medical equipment in hospitals while adhering to relevant industry standards.
Bioinformatics is considered both an umbrella term for the body of biological studies that use computer programming as part of their methodology, as well as a reference to specific analysis "pipelines" that are repeatedly used, particularly in the field of genomics.
Often, such identification is made with the aim of better understanding the genetic basis of disease, unique adaptations, desirable properties (esp.
It has experienced steady and strong growth over its history, with many companies investing large amounts of money into the development of new products.
OCT, for example, uses light to create high-resolution, three-dimensional images of internal structures, such as the retina in the eye or the coronary arteries in the heart.
[9] Bioartificial organs, which use both synthetic and biological component, are also a focus area in research, such as with hepatic assist devices that use liver cells within an artificial bioreactor construct.
This is an extremely broad category—essentially covering all health care products that do not achieve their intended results through predominantly chemical (e.g., pharmaceuticals) or biological (e.g., vaccines) means, and do not involve metabolism.
Beyond modeling organs and the human body, emerging engineering techniques are also currently used in the research and development of new devices for innovative therapies,[12] treatments,[13] patient monitoring,[14] of complex diseases.
This area deals with enabling clinicians to directly or indirectly "view" things not visible in plain sight (such as due to their size, and/or location).
The system uses an external field generator and several EM passive sensors enabling scaling of the display to the patient's body contour, and a real-time view of the feeding tube tip location and direction, which helps the medical staff ensure the correct placement in the GI tract.
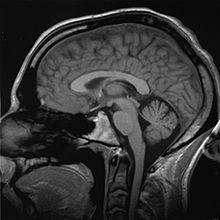
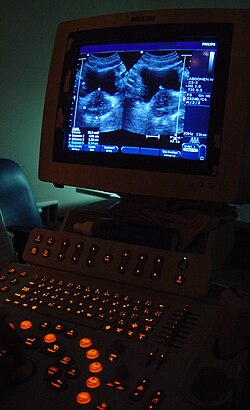
[15] Imaging technologies are often essential to medical diagnosis, and are typically the most complex equipment found in a hospital including: fluoroscopy, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), nuclear medicine, positron emission tomography (PET), PET-CT scans, projection radiography such as X-rays and CT scans, tomography, ultrasound, optical microscopy, and electron microscopy.
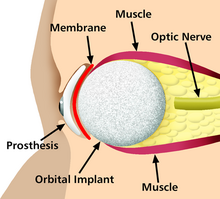
The surface of implants that contact the body might be made of a biomedical material such as titanium, silicone or apatite depending on what is the most functional.
Concerned with the intricate and thorough study of the properties and function of human body systems, bionics may be applied to solve some engineering problems.
Careful study of the different functions and processes of the eyes, ears, and other organs paved the way for improved cameras, television, radio transmitters and receivers, and many other tools.
In their various roles, they form a "bridge" between the primary designers and the end-users, by combining the perspectives of being both close to the point-of-use, while also trained in product and process engineering.
Functional areas addressed through rehabilitation engineering may include mobility, communications, hearing, vision, and cognition, and activities associated with employment, independent living, education, and integration into the community.
[10] The rehabilitation process for people with disabilities often entails the design of assistive devices such as Walking aids intended to promote the inclusion of their users into the mainstream of society, commerce, and recreation.
According to U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Class I recall is associated to "a situation in which there is a reasonable probability that the use of, or exposure to, a product will cause serious adverse health consequences or death"[17] Regardless of the country-specific legislation, the main regulatory objectives coincide worldwide.
A product is safe if patients, users, and third parties do not run unacceptable risks of physical hazards (death, injuries, ...) in its intended use.
Protective measures have to be introduced on the devices to reduce residual risks at an acceptable level if compared with the benefit derived from the use of it.
Effectiveness is achieved through clinical evaluation, compliance to performance standards or demonstrations of substantial equivalence with an already marketed device.
This requires that a quality system shall be in place for all the relevant entities and processes that may impact safety and effectiveness over the whole medical device lifecycle.
The paramount objectives driving policy decisions by the FDA are safety and effectiveness of healthcare products that have to be assured through a quality system in place as specified under 21 CFR 829 regulation.
RoHS seeks to limit the dangerous substances in circulation in electronics products, in particular toxins and heavy metals, which are subsequently released into the environment when such devices are recycled.
For the first time, not only manufacturers but also importers and distributors share a responsibility to ensure Electrical and Electronic Equipment within the scope of RoHS complies with the hazardous substances limits and have a CE mark on their products.
Biomedical engineering has only recently been emerging as its own discipline rather than a cross-disciplinary hybrid specialization of other disciplines; and BME programs at all levels are becoming more widespread, including the Bachelor of Science in Biomedical Engineering which includes enough biological science content that many students use it as a "pre-med" major in preparation for medical school.
They may also feature extensive collaborative efforts with programs in other fields (such as the university's Medical School or other engineering divisions), owing again to the interdisciplinary nature of BME.
By virtue of its extensive biotechnology sector, its numerous major universities, and relatively few internal barriers, the U.S. has progressed a great deal in its development of BME education and training opportunities.
Europe, which also has a large biotechnology sector and an impressive education system, has encountered trouble in creating uniform standards as the European community attempts to supplant some of the national jurisdictional barriers that still exist.