Emerging technologies
Emerging technologies are characterized by radical novelty (in application even if not in origins), relatively fast growth, coherence, prominent impact, and uncertainty and ambiguity.
In other words, an emerging technology can be defined as "a radically novel and relatively fast growing technology characterised by a certain degree of coherence persisting over time and with the potential to exert a considerable impact on the socio-economic domain(s) which is observed in terms of the composition of actors, institutions and patterns of interactions among those, along with the associated knowledge production processes.
Convergence brings previously separate technologies such as voice (and telephony features), data (and productivity applications) and video together so that they share resources and interact with each other, creating new efficiencies.
Many writers, including computer scientist Bill Joy,[5] have identified clusters of technologies that they consider critical to humanity's future.
They could use it as "good shepherds" for the rest of humanity or decide everyone else is superfluous and push for the mass extinction of those made unnecessary by technology.
Some thinkers, including environmental ethicist Bill McKibben, oppose the continuing development of advanced technology partly out of fear that its benefits will be distributed unequally in ways that could worsen the plight of the poor.
[10] By contrast, inventor Ray Kurzweil is among techno-utopians who believe that emerging and converging technologies could and will eliminate poverty and abolish suffering.
[11] Some analysts such as Martin Ford, author of The Lights in the Tunnel: Automation, Accelerating Technology and the Economy of the Future,[12] argue that as information technology advances, robots and other forms of automation will ultimately result in significant unemployment as machines and software begin to match and exceed the capability of workers to perform most routine jobs.
This may result in substantial unemployment at all skill levels, stagnant or falling wages for most workers, and increased concentration of income and wealth as the owners of capital capture an ever-larger fraction of the economy.
This in turn could lead to depressed consumer spending and economic growth as the bulk of the population lacks sufficient discretionary income to purchase the products and services produced by the economy.
The central functions (or goals) of AI research include reasoning, knowledge, planning, learning, natural language processing (communication), perception and the ability to move and manipulate objects.
There is an enormous number of tools used in AI, including versions of search and mathematical optimization, logic, methods based on probability and economics, and many others.
[18] Gene therapy was first successfully demonstrated in late 1990/early 1991 for adenosine deaminase deficiency, though the treatment was somatic – that is, did not affect the patient's germ line and thus was not heritable.
It received U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for use in the treatment of advanced prostate cancer patients on April 29, 2010.
Despite the promising outcomes of this innovative technology, CAR-T cells are not exempt from limitations that must yet to be overcome in order to provide reliable and more efficient treatments against other types of cancer.
Early prototypes include the McDonnell Douglas DC-X tested in the 1990s,[37] but the company SpaceX was the first to use propulsive reusability on the first stage of an operational orbital launch vehicle, the Falcon 9, in the 2010s.
It accesses and uses some part of the research communities' (the academia's) accumulated theories, knowledge, methods, and techniques, for a specific, often state-, business-, or client-driven purpose.
Patents provide inventors with a limited period of time (minimum of 20 years, but duration based on jurisdiction) of exclusive right in the making, selling, use, leasing or otherwise of their novel technological inventions.
It was followed, again in market size, by big data technologies, robotics, AI, 3D printing and the fifth generation of mobile services (5G).
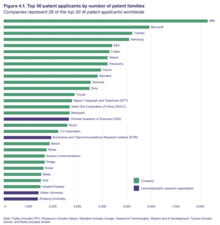
Companies represent 26 out of the top 30 AI patent applicants, with universities or public research organizations accounting for the remaining four.
Its purpose was to formulate and execute research and development projects to expand the frontiers of technology and science, with the aim to reach beyond immediate military requirements.
The XPRIZE series of awards, public competitions designed and managed by the non-profit organization called the X Prize Foundation, are intended to encourage technological development that could benefit mankind.
In 2003, David Gobel seed-funded the Methuselah Mouse Prize (Mprize) to encourage the development of new life extension therapies in mice, which are genetically similar to humans.
[43] The first documented example of this term being used dates to early 1983, when an unnamed banking executive was quoted to have used it in reference to Storage Technology Corporation.