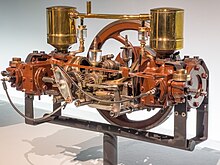
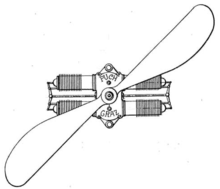
Flat engine
The advantages of flat engines are a short length, low centre of mass and suitability for air cooling (due to the well-exposed, large-surface-area cylinders and cylinder heads, and their short length).
[2] The most common usages of flat engines are: Most flat engines use a "boxer" configuration, where each pair of opposing pistons move inwards and outwards at the same time, somewhat like boxing competitors punching their gloves together before a fight.
[3] Boxer engines have low vibration, being they are the only common configuration that has no unbalanced forces, regardless of the number of pairs of cylinders.
However, a rocking couple is present, since each cylinder is slightly offset from the other member of its pair due to the distance between the crankpins along the crankshaft.
Designed by Norbert Riedel, these engines have a very oversquare stroke ratio of 2:1 so that they could fit within the intake diverter, directly forward of the turbine compressor.
[citation needed] Flat engines offer several advantages for motorcycles including a low centre of mass, low vibration, suitability for shaft drive, and equal cooling of the cylinders (for air-cooled engines).
[8] When used in cars, advantages of flat engines are a low centre of mass (which improves the handling of the car),[4] short length, low vibration and suitability for air cooling (due to the well exposed, large surface area, cylinder heads and short length).
[citation needed] Flat engines were used by various automobile manufacturers – mostly with a boxer-four design – up until the late 1990s.
The opposite layout, front-engine front-wheel drive, was also common for cars with flat engines.
The traditional front-engine, rear-wheel-drive layout is relatively uncommon for cars with flat engines, however some examples include the Toyota 86 / Subaru BRZ (2012–present), Jowett Javelin (1947–1953), Glas Isar (1958–1965) and the Tatra 11 (1923–1927).
Chevrolet used a horizontally opposed air-cooled 6 cylinder engine in its Corvair line during its entire production run from 1960 to 1969 in various applications and power ratings, including one of the first uses of a turbocharger in a mass-produced automobile.
[14] Most of Subaru's models are powered by a boxer-four engine in either naturally aspirated or turbocharged form.