British Army during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
His department, the War Office, controlled troop movements, facilities and pay rates, while he was accountable to Parliament for the costs of the army and had to settle disputes arising from the clash of civilian and military interests (e.g. billeting).
During the course of the wars against Napoleon, the British armed forces were expanded by subsequent Acts of Parliament, often by raising additional battalions for existing regiments, so that the effective strength of the infantry increased threefold between 1793 and 1801.
Most soldiers at the time signed on for life in exchange for a "bounty" of £23 17s 6d, a lot of which was absorbed by the cost of outfitting "necessities" but a system of 'limited service' (seven years for infantry, ten for cavalry and artillery) was introduced in 1806 to attract recruits.
Soldiers began, from 1800 onward, to receive a daily beer money allowance in addition to their regular wages; the practice was started on the orders of the Duke of York.
This deficiency largely persisted until Lieutenant-General John Moore began teaching his developed system of drill and maneuvers at Shorncliffe Army Camp in 1803.
As the wars progressed line infantry tactics were developed to allow more flexibility for command and control, placing more reliance upon the officers on the spot for quick reactions.
It was decommissioned on 12 July 1802, after the Peace of Amiens, after which most personnel (but not all) returned to the Batavian Republic, under an amnesty in connection with that treaty.The Dutch Emigrant Artillery was formed in Hanover in 1795 from remnants of Franco-Dutch units.
[14]Soldiers were allowed to marry, but wives were expected to submit to army rules and discipline, as well to contribute to regimental affairs by performing washing, cooking and other duties.
The treatments for such ailments were sometimes unusual: for example, an infusion of rue, sage, mint, rosemary and wormwood in strong vinegar was recommended as a cure for typhoid fever, to which camphor dissolved in brandy was added.
After some initial setbacks, Cornwallis was ultimately victorious capturing the Mysorean capital city of Seringapatam and compelling Mysore to make peace on terms favourable to Britain.
The Allies then established a new front in southern Holland and Germany, but with poor co-ordination and failing supplies were forced to continue their retreat through the arduous winter of 1794/5.
The campaign exposed many shortcomings in the British army, especially in discipline and logistics, which had developed in the ten years of peacetime neglect since the American War of Independence.
[41] The islands of Martinique, Guadeloupe and several ports in Saint-Domingue were captured in 1794 and 1795 by expeditionary forces under General Charles Grey, but the British units were almost exterminated by disease.
[42] Eight thousand reinforcements under Lieutenant General Sir Ralph Abercromby arrived in 1796, and secured many French territories, and those of Spain and the Netherlands (which was now titled the Batavian Republic and allied to France).
In 1795 a combined British army and Royal Navy force under the command of Major-General James Craig and Admiral Elphinstone captured the Dutch Cape Colony.
After careful preparations and rehearsals in Turkish anchorages, a British force under Sir Ralph Abercromby made a successful opposed landing at the Battle of Abukir (1801).
In 1805, as part of the manoeuvres which ultimately led to the Battle of Trafalgar, a French fleet carrying 6,500 troops briefly captured Dominica and other islands but subsequently withdrew.
The naval commander of the expedition, Admiral Home Riggs Popham then conceived the idea of occupying the Spanish Plate River colonies.
A detachment under Major General William Carr Beresford occupied Buenos Aires for six weeks, but was expelled by Spanish troops and local militias.
In 1807 an army and navy expedition under the command of General Alexander Mackenzie Fraser was dispatched with the objective of capturing the Egyptian city of Alexandria to secure a base of operations to disrupt the Ottoman Empire.
To provide a diversion, a British force consisting mainly of the troops recently evacuated from Corunna was dispatched to capture the Dutch ports of Flushing and Antwerp.
In spring 1813, Wellington resumed the offensive, leaving Portugal and marching northwards through Spain, dropping the lines of communication to Lisbon and establishing new ones to the Spanish ports on the Bay of Biscay.
At the Battle of Vitoria the French armies were routed, disgorging an enormous quantity of loot, which caused the British troops to abandon the pursuit and break ranks to plunder.
[48][49] On 31 March 1814, allied armies entered Paris, and Napoleon abdicated on 6 AprilThe news was slow to reach Wellington, who fought the indecisive Battle of Toulouse on 10 April.
Multiple US invasions north of the border were repulsed; such an example can be seen at the Battle of Crysler's Farm in which battalions of 89th and 49th Regiments attacked and routed a significantly larger American force making its way toward Montreal.
Before news of it could reach the armies on the other side of the Atlantic, a British force under Wellington's brother-in-law Sir Edward Pakenham was defeated foolhardily attacking heavily fortified positions at the Battle of New Orleans.
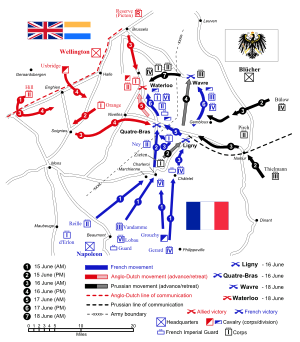
On 16 June 1815, Napoleon himself led men against Blücher at Ligny, while Marshall Ney commanded an attack against Wellington's forward army at the Battle of Quatre Bras.
Here British and Nassau troops stubbornly defended the Hougomont buildings all day; the action eventually engaging a whole French Corps which failed to capture the Chateau.
At half past one, the Anglo-Allied Army was assaulted by d'Erlon's infantry attack on the British left wing but the French were forced back with heavy losses.
Over the following decades, various regiments were added, removed or reformed to respond to military or colonial needs, but it never grew particularly large again until the First World War, and the Empire became more reliant on local forces to maintain defence and order.