COVID-19 pandemic in the Czech Republic
On 12 January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed that a novel coronavirus was the cause of a respiratory illness in a cluster of people in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China, which was reported to the WHO on 31 December 2019.
A 2022 study published in the Scientific Reports has shown the registered numbers of deaths in the Czech Republic is approximately “3.5 times lower than it would be expected without vaccination”.
[29] 3 March – Another case was reported, a woman from Ecuador studying in Milano, a friend of the U.S. tourist who tested positive several days prior.
[5] The Czech Republic became one of the first[42] countries in the EU to completely close its borders (with exemptions including international freight transport, see policies section below).
According to Security Information Service, the shortage happened after Chinese embassy conducted massive purchases of respirators available on Czech market during January and February and transferred them to China.
[54] An Antonov An-124 Ruslan provided through the NATO Support and Procurement Agency arrived again with 24 tons of medical products purchased by the Czech government in China.
[67] 30 March – In South Moravia, testing of the so-called "smart quarantine" was started: local travel history of infected persons were to be tracked using data from mobile phones and bank cards.
Three hundred military personnel were deployed to reinforce local health authority for the purpose of tracing patients' contacts and collecting samples.
If this approach is deemed successful by the authorities for diminishing the pandemic, the "smart quarantine" method is planned to replace the existing nationwide curfew policy.
The by-election to fill a seat after Jaroslav Kubera, who died of heart attack, was originally planned on 27 March and would take place on 5 June.
A large number of Czech Romanis started returning from particularly hit United Kingdom, where many lived for over 15 years, leading to fear of possible increase of COVID-19 infection.
[94][95] Hyundai factory in Nošovice, which makes 1,500 cars a day including Kona Electric, restarted production after three weeks' pause.
Ten days later, Government exempted Korean Hyundai "specialists and key workers" needed for ramp up of electric vehicle production from cross-border and quarantine restrictions.
[101] 24 April – In line with the decision of the Municipal Court of Prague, the Government announced that it would seek Chamber of Deputies' consent to extend the State of Emergency until 25 May.
Apart from the coal mining hotspot, authorities deemed situation in the rest of the country as stable, except for Prague where they identified several small clusters with community spread.
[114] To combat an uptick in coronavirus cases in the country, Institute of Health Information and Statistics presented the Czech regional traffic light rating system, which has four levels.
[116] The Czech PM Andrej Babiš nixes the preventive face mask regulations established by Health Ministry, which were supposed to come in place when children return to school after the holidays on 1 September.
Schools, kindergartens and playgrounds are excluded from restrictions[120] Belgium has placed Prague on its list of "red" risk zones, requiring a mandatory two-week quarantine on arrival for incoming travellers from the Czech capital.
[120] 18 September – The Czech Republic reported more than 3,000 cases in a single day for the first time[121] The wearing of face masks is now mandatory in all interior spaces of universities.
A restriction on tuition in the form of a switch to distance learning is to apply to secondary and higher vocational schools and universities in regions with a red or amber.
Dining establishments will be limited to 4 people at one table, and pupils in the upper level of elementary schools will alternate in-class and distance learning.
[135] 18 October – A Sunday-afternoon demonstration against the Czech government's anti-coronavirus restrictions ended in dramatic clashes between protesters and the police after the rally was officially terminated.
Resulting in 144 arrests and dozens of injuries[136] 20 October – Face masks again become mandatory at outdoor locations in cities, towns and villages where people are less than two meters apart.
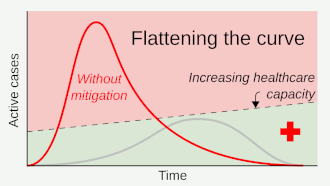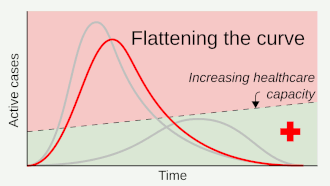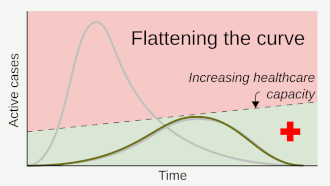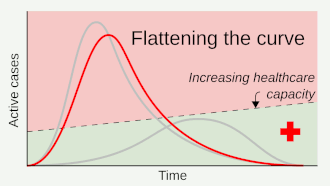
[140][circular reference] The main priority of affected nations currently is to move to a slower doubling time of new cases, to ensure less crowded hospitals and therefore a lower case-fatality rate.
Also, the national community's commitment to supporting/tolerating the restrictions and following the advice of health authorities plays an important role in the success of flattening the epidemic curve and limiting the spread of the virus.
List of selected countries subject to daily updates, as of the day of measure adoption they are: China, South Korea, Iran, Italy, Spain, Austria, Germany, Switzerland, Sweden, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, Great Britain, Denmark, and France.
Most other measures adopted "indefinitely" remain in force only as long as the State of Emergency lasts, as without it the Government lacks the constitutional authority to limit the associated rights.
List of selected countries subject to daily updates, as of the day of ban entry into force they were China, South Korea, Iran, Italy, Spain, Austria, Germany, Switzerland, Sweden, Norway, the Netherlands, Belgium, Great Britain, Denmark, and France.
(revocation)[267] Deadline for Income Tax submission moved by 3 months for natural persons (new date is 1 July) Banks will provide an option of delaying loan payments for people and small businesses affected by the coronavirus Firearm registrations deemed non-essential by the Ministry of Interior Explanatory Note, as part of the general suspension of non-essential visits to government offices.
Gun licence holders instructed to merely inform police about a purchase by post or electronic communication and visit station for registration after the end of curfew.