COVID-19 pandemic in Oceania
[3][4][5] As a result of the high transmissibility of the Delta variant however, by August 2021, the Australian states of New South Wales and Victoria had conceded defeat in their eradication efforts.
Note: The statistical information in this table may vary from official reports and WHO data, and is known to inconsistently include historical and suspected cases which may have returned a positive diagnostic test result.
In some cases, these positive test results were reported by the media and/or by the relevant health authorities as confirmed cases, but this is not necessarily indicative of active SARS-CoV-2 infection due to most COVID-19 tests analysing past presence of the virus through the detection of relevant antibodies or through the detection of one or more viral fragments which are slowly shed during or after a person's recovery.
[70][71][72] Australian borders were closed to all non-residents from 20 March 2020; all returning travellers are required to undergo two weeks' quarantine in hotels.
From March onwards, many states and territories also closed their internal borders, with similar quarantine requirements for exempt travellers.
A breach of quarantine in hotels across Victoria led to the state experiencing a second wave and returning to strict lockdown measures from July through to October 2020, successfully waning the spread of the virus.
[73][74] No deaths from COVID-19 were recorded in Australia from 28 December 2020 until 13 April 2021, when an overseas returned traveller died at The Prince Charles Hospital, Brisbane.
In late August 2021, Victoria also reported its first deaths since the end of the outbreak in June 2020 that saw the longest lockdown period in Australia at the time.
[76][77][78] In response to rising cases, both New South Wales [79] and Victoria [80] underwent extended lockdowns, taking 107 and 77 days respectively, with both states opening up in October 2021.
[81] Beginning in December 2021, Australia has experienced a major outbreak of the Omicron variant, with significantly higher case numbers than at any other time of the pandemic.
[83] In March 2020, as a precautionary measure, the Norfolk Island Regional Council imposed a 32-day travel ban and declared a state of emergency.
[84] Administrator Eric Hutchinson stated that the measures were necessary due to the remote island's extremely limited health capacity.
[109] On 1 February 2020, the government of Kiribati put all visas from China on hold and required new arrivals to fill in a health form and travellers from countries with the coronavirus to go through a self-quarantine period.
[111] On 10 September 2020, the government announced it will keep the borders closed until the end of the year to keep the country free of the virus.
[116] On 1 March, the ban was extended to China, Macau, Hong Kong, Japan, South Korea, Italy, and Iran.
[118] The first two positive cases of COVID-19 were confirmed at the US Army Garrison on Kwajalein Atoll (USAG-KA) on 29 October.
[121][122] The suspected case was later deemed to be non-infectious and a detection of historical viral fragments after the individual returned negative antibody and antigen tests later in the month.
[125] The government declared a national emergency as a preventive measure, suspending all but one weekly flight to the country and instituting a 14-day quarantine for all arrivals.
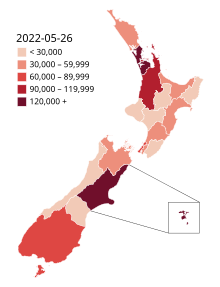
[146] Due to the reduction in community transmissions, lockdown restrictions in Auckland and the rest of New Zealand were progressively eliminated on 30 August,[147] 23 September,[148] and 7 October 2020.
[153] In early October 2021, Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern confirmed that New Zealand's elimination strategy would be phased out in favour of a new model that takes into account the country's vaccination rates.
[7][8] In November 2021, a Māori tribe asked anti-vaxxers to stop using the Ka Mate haka to promote their protests.
[154] On 5 June 2021, the first positive PCR test result in the Cook Islands was obtained which was reported in the media.
[165] The President of Palau Thomas Remengesau Jr. issued an executive order suspending all charter flights from China, Macau, and Hong Kong from 1–29 February 2020.
[165] As a signatory of the Compact of Free Association with the United States, Palau has received vaccines from Operation Warp Speed.
[183] On 29 October, Tonga reported its first case; a seasonal worker returning from Christchurch in New Zealand.
[186] While the epicenter of COVID-19 in the USA lies in the contiguous 48 states, cases and outbreaks have been reported in the country's Oceanic jurisdictions.
The state of Hawaii has by far the most coronavirus cases in the region, followed up by the territories of Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands.
[189] By 28 August 2020, the US territory of Guam has had 1,287 confirmed cases of the virus, 488 recoveries, and ten deaths.
[192] In response to the initial spike in coronavirus cases, Governor David Ige issued a state-wide lockdown, which lasted from 24 March to 30 April.
[200] On 11 November 2020, Vanuatu recorded its first COVID case by a man who tested positive after returning from the United States via Auckland and Sydney.