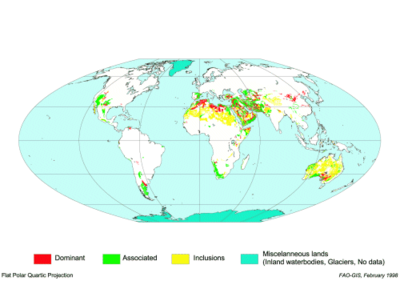
Calcisol
Calcisols are common in calcareous parent materials and widespread in arid and semi-arid environments.
Dryness, and in places also stoniness and/or the presence of a shallow petrocalcic horizon, limit the suitability of Calcisols for agriculture.
If irrigated, drained (to prevent salinisation) and fertilised, Calcisols can be highly productive under a wide variety of crops.
Hilly areas with Calcisols are predominantly used for low volume grazing of cattle, sheep and goats.
The total Calcisol area may well amount to some 10 million square kilometres, nearly all of it in the arid and semi-arid subtropics of both hemispheres.