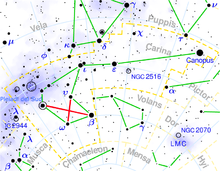
Carina (constellation)
Carina was once a part of Argo Navis, the great ship of the mythical Jason and the Argonauts who searched for the Golden Fleece.
Therefore, Carina has the α, β and ε, Vela has γ and δ, Puppis has ζ, and so on.
[5] Carina contains Canopus, a white-hued supergiant that is the second-brightest star in the night sky at magnitude −0.72.
Beta Carinae, traditionally called Miaplacidus, is a blue-white-hued star of magnitude 1.7, 111 light-years from Earth.
Epsilon Carinae is an orange-hued giant star similarly bright to Miaplacidus at magnitude 1.9; it is 630 light-years from Earth.
[3] It was first discovered to be unusual in 1677, when its magnitude suddenly rose to 4, attracting the attention of Edmond Halley.
Its most prominent outburst made Eta Carinae the equal of Sirius; it brightened to magnitude −1.5 in 1843.
[12] The Keyhole is about seven light-years wide and is composed mostly of ionized hydrogen, with two major star-forming regions.
Eta Carinae is so massive that it has reached the theoretical upper limit for the mass of a star and is therefore unstable.
Because of this instability and history of outbursts, Eta Carinae is considered a prime supernova candidate for the next several hundred thousand years because it has reached the end of its estimated million-year life span.
[11] NGC 2516 is an open cluster that is both quite large[13] (approximately half a degree square) and bright, visible to the unaided eye.
Superimposed on the cluster is Chi Carinae, a yellow-white-hued star of magnitude 3.9, far more distant than NGC 3532.
[11] Carina contains the radiant of the Eta Carinids meteor shower, which peaks around January 21 each year.
The Māori name Ariki ("High-born"),[14] and the Hawaiian Ke Alii-o-kona-i-ka-lewa, "The Chief of the southern expanse"[15] both attest to the star's prominence in the southern sky, while the Māori Atutahi, "First-light" or "Single-light", and the Tuamotu Te Tau-rari and Marere-te-tavahi, "He who stands alone".
It was also called Kapae-poto ("Short horizon"), because it rarely sets from the vantage point of New Zealand,[17] and Kauanga ("Solitary"), when it was the last star visible before sunrise.
Due to precession of Earth's axis, by the year 4700 the south celestial pole will be in Carina.
[19] USS Carina (AK-74) was a United States Navy Crater-class cargo ship named after the constellation.