Chandra X-ray Observatory
In response to a decrease in NASA funding in 2024 by the US Congress, Chandra is threatened with an early cancellation despite having more than a decade of operation left.
A group of astronomers have put together a public outreach project to try to get enough American citizens to persuade the US Congress to provide enough funding to avoid early termination of the observatory.
[8] In 1976, the Chandra X-ray Observatory (called AXAF at the time) was proposed to NASA by Riccardo Giacconi and Harvey Tananbaum.
This eliminated the possibility of improvement or repair by the Space Shuttle but put the observatory above the Earth's radiation belts for most of its orbit.
AXAF was assembled and tested by TRW (now Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems) in Redondo Beach, California.
[13] At 22,753 kilograms (50,162 lb),[1] it was the heaviest payload ever launched by the shuttle, a consequence of the two-stage Inertial Upper Stage booster rocket system needed to transport the spacecraft to its high orbit.
It is operated by the SAO at the Chandra X-ray Center in Cambridge, Massachusetts, with assistance from MIT and Northrop Grumman Space Technology.
[17] ESA later resurrected a downsized version of the project as the Advanced Telescope for High Energy Astrophysics (ATHENA), with a proposed launch in 2028.
[19][20] Within days, the 3-second error in data from one gyro was understood, and plans were made to return Chandra to full service.
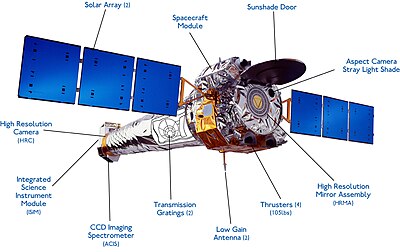
[47] The thick substrate and particularly careful polishing allowed a very precise optical surface, which is responsible for Chandra's unmatched resolution: between 80% and 95% of the incoming X-ray energy is focused into a one-arcsecond circle.
However, the thickness of the substrate limits the proportion of the aperture which is filled, leading to the low collecting area compared to XMM-Newton.
[50] Other navigation and orientation systems on board CXO include an aspect camera, Earth and Sun sensors, and reaction wheels.
The transmission gratings, which swing into the optical path behind the mirrors, provide Chandra with high resolution spectroscopy.


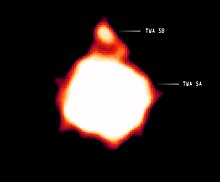


Chandra · Earth