Chlamydomonas
[3] Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism for molecular biology, especially studies of flagellar motility and chloroplast dynamics, biogenesis, and genetics.
One of the many striking features of Chlamydomonas is that it contains ion channels (channelrhodopsins) that are directly activated by light.
[4] Molecular phylogeny studies indicated that the traditional genus Chlamydomonas as defined using morphological data, was polyphyletic within Volvocales.
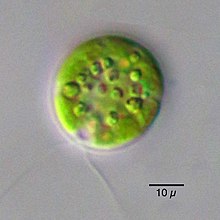
Cells are generally spherical to cylindrical in shape, but may be elongately spindle-shaped,[9] and a papilla may be present or absent.
Most species are obligate phototrophs but C. reinhardtii and C. dysostosis are facultative heterotrophs that can grow in the dark in the presence of acetate as a carbon source.