County
The term is derived from the Old French comté denoting a jurisdiction under the sovereignty of a count (earl) or, in his stead, a viscount (vicomte).
Although there were at first no counts, vicomtes or counties in Anglo-Norman England, the earlier Anglo-Saxons did have earls, sheriffs and shires.
Examples include the United States and Canada, which evolved from British colonial North America and inherited British governmental traditions, where counties often remain as local administrative divisions that evolved from historic (pre-federal) counties governed by courts/magistracy.
It remains one of the oldest titles of local-level government in China and significantly predates the establishment of provinces in the Yuan dynasty (1279–1368).
Above county, there are special municipalities (in effect) and province (suspended due to economical and political reasons).
Nowadays, most counties in mainland China, i.e. with "Xian" in their titles, are administered by prefecture-level cities and have mainly agricultural economies and rural populations.
A regency is headed by a regent who is directly elected by the people, and is responsible for public services such as education, health, and infrastructure.
Fars province has the highest number of shahrestāns, with 36, while Qom uniquely has one, being coextensive with its namesake county.
County is the common English translation for the character 군 (gun or kun) that denotes the current second level political division in South Korea.
The two names are used interchangeably ('megye' used in common parlance, and when referring to the counties of other states), just like before 1950, when the word 'megye' even appeared in legal texts.
Counties are subdivided into districts (járás) and municipalities, the two types of which are towns (város) and villages (község), each one having their own elected mayor and council.
Historically, the counties of Meath and Westmeath and small parts of surrounding counties constituted the province of Mide, which was one of the "Five Fifths" of Ireland (in the Irish language the word for province, cúige, means 'a fifth': from cúig, 'five'); however, these have long since been absorbed into Leinster.
However, in the north as well as in the south, the traditional 32 counties and 4 provinces remain in common usage for many sporting, cultural and other purposes.
In the context of pre-modern Italy, the Italian word contado generally refers to the countryside surrounding, and controlled by, the city state.
In contemporary usage, contado can refer to a metropolitan area, and in some cases large rural/suburban regions providing resources to distant cities.
In historical contexts this may be confusing because the Polish term hrabstwo (a territorial unit administered/owned by a hrabia, count) is also literally translated as "county" and it was subordinated under powiat.
[14] Counties were retained by the independent Ukrainian People's Republic of 1917–1921, and in Czechoslovakia, Poland, and Romania until the Soviet annexations at the start of World War II.
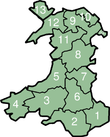
Modern local government in Scotland, Wales, Northern Ireland and a large part of England is trending towards smaller unitary authorities: a system similar to that proposed in the 1960s by the Redcliffe-Maud Report for most of Britain.
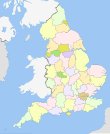
In England, in the Anglo-Saxon period, shires were established as areas used for the raising of taxes, and usually had a fortified town at their centre.
In the medieval period, a number of important cities were granted the status of counties in their own right, such as London, Bristol and Coventry, and numerous small exclaves such as Islandshire were created.
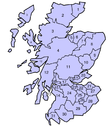
[17] In the Gaelic form, Scottish traditional county names are generally distinguished by the designation siorramachd—literally "sheriffdom", e.g. Siorramachd Earra-ghaidheal (Argyllshire).
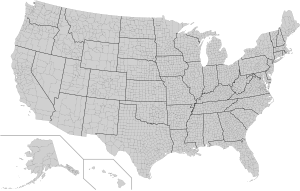
The primary administrative division of Southern Ontario is its 22 counties, which are upper-tier local governments providing limited municipal services to rural and moderately dense areas—within them, there are a variety of lower-tier towns, cities, villages, etc.
Washington, D.C., is known as a federal city because it is outside the jurisdiction of any state; the U.S. Census Bureau treats it as a single county equivalent.
County governments in Rhode Island and Connecticut have been completely abolished but the entities remain for administrative and statistical purposes.
[22] By way of contrast, Massachusetts, with far less territory, has massively sized counties in comparison even to Pennsylvania's largest,[c] yet each organizes their judicial and incarceration officials similarly.
An LGA functions basically the same way as a county of other countries, although it is called instead as "city", "municipality", "shire", "borough", "town", "district" or simple "councils" depending on the state/territory and subregion.
It performs municipal services and regulates permits for land uses, but lacks any legislative or law enforcement powers.
They had chairmen, not mayors as boroughs and cities had; many legislative provisions (such as burial and land subdivision control) were different for the counties.
The Local Government Act 1974 began the process of bringing urban, mixed, and rural councils into the same legislative framework.
States in Brazil were divided into microregions (Portuguese: microrregiões) before they were replaced by "immediate geographic regions" in 2017.