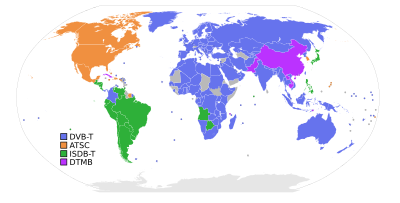
Digital Terrestrial Multimedia Broadcast
It is used there and in both of their special administrative regions (Hong Kong and Macau), and also in Cambodia, the Comoros, Cuba, East Timor, Laos, Vietnam, and Pakistan.
[2] Previously known as DMB-T/H (Digital Multimedia Broadcast-Terrestrial/Handheld), the DTMB is a merger of the standards ADTB-T (developed by the Shanghai Jiao Tong University), DMB-T (developed by Tsinghua University), and TiMi (Terrestrial Interactive Multiservice Infrastructure); this last one is the standard proposed by the Academy of Broadcasting Science in 2002.
DTMB system is compatible with fixed reception (indoor and outdoor) and mobile digital terrestrial television.
For example, a pseudo-random noise code (PN) as a guard interval that allows faster synchronization system and a more accurate channel estimation, Low-Density Parity Check (LDPC) for error correction, modulation Time Domain Synchronization - Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (TDS-OFDM), which allows the combination of broadcasting in SD, HD, and multimedia services, etc.
It combines information from the body and the head to form the frame and this is passed through the SRRC (Square Root Raised Cosine) filter to become a signal within an 8 MHz channel bandwidth.