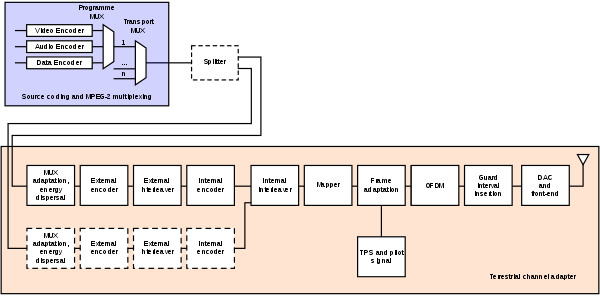
DVB-T
It is also the format widely used worldwide (including North America) for Electronic News Gathering for transmission of video and audio from a mobile newsgathering vehicle to a central receive point.
The DVB-T Standard is published as EN 300 744, Framing structure, channel coding and modulation for digital terrestrial television.
These include the D-book in the UK, the Italian DGTVi,[9] the ETSI E-Book and the Nordic countries and Ireland NorDig.
DVB-T has been further developed into newer standards such as DVB-H (Handheld), which was a commercial failure and is no longer in operation, and DVB-T2, which was initially finalised in August 2011.
The longer the guard interval the larger is the potential SFN area without creating intersymbol interference (ISI).