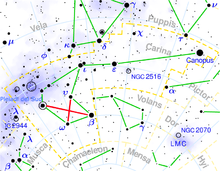
Carina (constellation)
Carina was once a part of Argo Navis, the great ship of the mythical Jason and the Argonauts who searched for the Golden Fleece.
Therefore, Carina has the α, β and ε, Vela has γ and δ, Puppis has ζ, and so on.
[5] Carina contains Canopus, a white-hued supergiant that is the second-brightest star in the night sky at magnitude −0.72.
Beta Carinae, traditionally called Miaplacidus, is a blue-white-hued star of magnitude 1.7, 111 light-years from Earth.
Epsilon Carinae is an orange-hued giant star similarly bright to Miaplacidus at magnitude 1.9; it is 630 light-years from Earth.
[3] It was first discovered to be unusual in 1677, when its magnitude suddenly rose to 4, attracting the attention of Edmond Halley.
Upsilon Carinae is a binary star with two blue-white-hued giant components, 1,600 light-years from Earth.
[12] The Keyhole is about seven light-years wide and is composed mostly of ionized hydrogen, with two major star-forming regions.
Eta Carinae is so massive that it has reached the theoretical upper limit for the mass of a star and is therefore unstable.
Because of this instability and history of outbursts, Eta Carinae is considered a prime supernova candidate for the next several hundred thousand years because it has reached the end of its estimated million-year life span.
[11] NGC 2516 is an open cluster that is both quite large[13] (approximately half a degree square) and bright, visible to the unaided eye.
Superimposed on the cluster is Chi Carinae, a yellow-white-hued star of magnitude 3.9, far more distant than NGC 3532.
[11] Carina contains the radiant of the Eta Carinids meteor shower, which peaks around January 21 each year.
The Māori name Ariki ("High-born"),[14] and the Hawaiian Ke Alii-o-kona-i-ka-lewa, "The Chief of the southern expanse"[15] both attest to the star's prominence in the southern sky, while the Māori Atutahi, "First-light" or "Single-light", and the Tuamotu Te Tau-rari and Marere-te-tavahi, "He who stands alone".
It was also called Kapae-poto ("Short horizon"), because it rarely sets from the vantage point of New Zealand,[17] and Kauanga ("Solitary"), when it was the last star visible before sunrise.
Due to precession of Earth's axis, by the year 4700 the south celestial pole will be in Carina.
[19] USS Carina (AK-74) was a United States Navy Crater-class cargo ship named after the constellation.