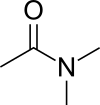
Dimethylacetamide
For this reason, it is used in gel permeation chromatography to determine the molar mass distribution of cellulose samples.
Dimethylacetamide is also used as an excipient in drugs, e.g. in Vumon (teniposide), Busulfex (busulfan) or Amsidine (amsacrine).
[8][9][10][11] At high doses (400 mg/kg body mass daily), dimethylacetamide causes effects on the central nervous system (e.g. depression, hallucinations and delusion).
[14] In 2011, dimethylacetamide was identified in the EU as a Substance of very high concern (SVHC) because of its reproductive toxicity.
[16] In 2015, the CNESST (Committee on Standards, Equity, Health and Safety at Work in Quebec) has adopted a tightened classification of dimethylacetamide:[17]