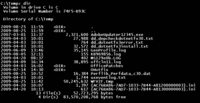
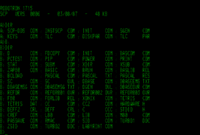
dir (command)
On some systems, a more graphical representation of the directory structure can be displayed using the tree command.
The command is available in the command-line interface (CLI) of the operating systems Digital Research CP/M,[2] MP/M,[3] Intel ISIS-II,[4] iRMX 86,[5] Cromemco CDOS,[6] MetaComCo TRIPOS,[7] DOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS,[8] IBM OS/2,[9] Microsoft Windows,[10] Singularity, Datalight ROM-DOS,[11] ReactOS,[12] GNU,[13] AROS[14] and in the DCL command-line interface used on DEC VMS, RT-11 and RSX-11.
The directory name is enclosed in double-quotes, to prevent it from being interpreted is as two separate command-line options because it contains a whitespace character.
The GNU operating system, however, has a dir command that "is equivalent to ls -C -b; that is, by default files are listed in columns, sorted vertically, and special characters are represented by backslash escape sequences".
The dir instruction, unlike ls -Cb, produces device-independent output.