Disk partitioning
IBM in its 1983 release of PC DOS version 2.0 was an early if not first use of the term partition to describe dividing a block storage device such as an HDD into physical segments.
[citation needed] Other terms used include logical disk,[4] minidisk,[5] portions,[6] pseudo-disk,[6] section,[6] slice[7] and virtual drive.
[5] With DOS, Microsoft Windows, and OS/2, a common practice is to use one primary partition for the active file system that will contain the operating system, the page/swap file, all utilities, applications, and user data.
On most Windows consumer computers, the drive letter C: is routinely assigned to this primary partition.
On Unix-based and Unix-like operating systems such as Linux, macOS, BSD, and Solaris, it is possible to use multiple partitions on a disk device.
Such a scheme has a number of advantages: A common minimal configuration for Linux systems is to use three partitions: one holding the system files mounted on "/" (the root directory), one holding user configuration files and data mounted on /home (home directory), and a swap partition.
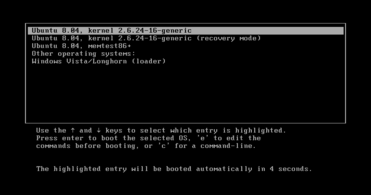
Multi-boot systems are computers where the user can boot into more than one distinct operating system (OS) stored in separate storage devices or in separate partitions of the same storage device.
The GUID Partition Table (Globally Unique IDentifier) is a part of the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) standard for the layout of the partition table on a physical hard disk.
[10] When a partition is deleted, its entry is removed from a table and the data is no longer accessible.
Some disk utilities may overwrite a number of beginning sectors of a partition they delete.
At startup, device drivers opened this file and assigned it a separate letter.
[13] This section describes the master boot record (MBR) partitioning scheme, as used historically in DOS, Microsoft Windows and Linux (among others) on PC-compatible computer systems.
The FAT16 and FAT32 file systems have made use of a number of partition type codes due to the limits of various DOS and Windows OS versions.
), they have all consistently used the same partition type code: 0x83 (Linux native file system).
It may be an operating system kernel image or bootloader or a completely separate piece of software.