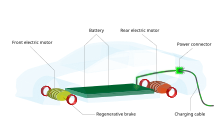
Dual-motor, four-wheel-drive layout
In automotive design, dual-motor, four-wheel-drive layout is mainly used by battery electric vehicles by having two electric motors that each drives the front and rear axle, creating a four-wheel drive layout.
This is made possible by the smaller size of electric motors compared to internal combustion engines (ICEs), which in addition are also accompanied by a bulky engine cooling system, allowing it to be fit more versatilely into multiple locations.
[1] The dual-motor layout is beneficial in re-distributing torque and power to maximize effective propulsion in response to road grip conditions and weight transfer in the vehicle.
[2] However dual-motor vehicles usually have less range for the same battery size than single-motor designs.
[4][5] A rare example of a non-electric vehicle utilizing this layout is the Citroën 2CV Sahara, which has two flat-twin petrol engines.