Earth
"[27] The name Terra /ˈtɛrə/ occasionally is used in scientific writing and especially in science fiction to distinguish humanity's inhabited planet from others,[28] while in poetry Tellus /ˈtɛləs/ has been used to denote personification of the Earth.
[41][42] Between approximately 4.0 and 3.8 Ga, numerous asteroid impacts during the Late Heavy Bombardment caused significant changes to the greater surface environment of the Moon and, by inference, to that of Earth.
[50] The presence of grains of the mineral zircon of Hadean age in Eoarchean sedimentary rocks suggests that at least some felsic crust existed as early as 4.4 Ga, only 140 Ma after Earth's formation.
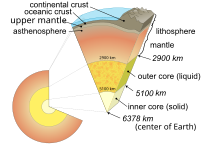
[56] New continental crust forms as a result of plate tectonics, a process ultimately driven by the continuous loss of heat from Earth's interior.
Over the period of hundreds of millions of years, tectonic forces have caused areas of continental crust to group together to form supercontinents that have subsequently broken apart.
Mammalian life has diversified over the past 66 Mys, and several million years ago, an African ape species gained the ability to stand upright.
[79] Earth's increasing surface temperature will accelerate the inorganic carbon cycle, possibly reducing CO2 concentration to levels lethally low for current plants (10 ppm for C4 photosynthesis) in approximately 100–900 million years.
[83] Even if the Sun were stable and eternal, a significant fraction of the water in the modern oceans would descend into the mantle, due to reduced steam venting from mid-ocean ridges as the core of the Earth slowly cools.
It is composed mostly of iron (32.1% by mass), oxygen (30.1%), silicon (15.1%), magnesium (13.9%), sulfur (2.9%), nickel (1.8%), calcium (1.5%), and aluminium (1.4%), with the remaining 1.2% consisting of trace amounts of other elements.
At approximately 3 Gyr, twice the present-day heat would have been produced, increasing the rates of mantle convection and plate tectonics, and allowing the production of uncommon igneous rocks such as komatiites that are rarely formed today.
[155][156] During magnetic storms and substorms, charged particles can be deflected from the outer magnetosphere and especially the magnetotail, directed along field lines into Earth's ionosphere, where atmospheric atoms can be excited and ionized, causing an aurora.
[177] The most widely accepted theory of the Moon's origin, the giant-impact hypothesis, states that it formed from the collision of a Mars-size protoplanet called Theia with the early Earth.
[185] Some theorists think that without this stabilization against the torques applied by the Sun and planets to Earth's equatorial bulge, the rotational axis might be chaotically unstable, exhibiting large changes over millions of years, as is the case for Mars, though this is disputed.
There are at least seven quasi-satellites, including 469219 Kamoʻoalewa, ranging in diameter from 10 m to 5000 m.[189][190] A trojan asteroid companion, 2010 TK7, is librating around the leading Lagrange triangular point, L4, in Earth's orbit around the Sun.
[215] Other atmospheric functions important to life include transporting water vapor, providing useful gases, causing small meteors to burn up before they strike the surface, and moderating temperature.
[216] This last phenomenon is the greenhouse effect: trace molecules within the atmosphere serve to capture thermal energy emitted from the surface, thereby raising the average temperature.
This water cycle is a vital mechanism for supporting life on land and is a primary factor in the erosion of surface features over geological periods.
Because unfixed hydrogen has a low molecular mass, it can achieve escape velocity more readily, and it leaks into outer space at a greater rate than other gases.
[244] Earth's life has also over time greatly diversified, allowing the biosphere to have different biomes, which are inhabited by comparatively similar plants and animals.
[248]Extreme weather, such as tropical cyclones (including hurricanes and typhoons), occurs over most of Earth's surface and has a large impact on life in those areas.
[249] Many places are subject to earthquakes, landslides, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, tornadoes, blizzards, floods, droughts, wildfires, and other calamities and disasters.
[252] This is driving changes such as the melting of glaciers and ice sheets, a global rise in average sea levels, increased risk of drought and wildfires, and migration of species to colder areas.
[253] Originating from earlier primates in Eastern Africa 300,000 years ago humans have since been migrating and with the advent of agriculture in the 10th millennium BC increasingly settling Earth's land.
Since the second half of the 20th century, some hundreds of humans have temporarily stayed beyond Earth, a tiny fraction of whom have reached another celestial body, the Moon.
[263] Most of these states together form the United Nations, the leading worldwide intergovernmental organization,[264] which extends human governance over the ocean and Antarctica, and therefore all of Earth.
[270] Earth's biosphere produces many useful biological products for humans, including food, wood, pharmaceuticals, oxygen, and the recycling of organic waste.
Through activities such as the burning of fossil fuels, humans have been increasing the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, altering Earth's energy budget and climate.
Of the nine identified boundaries, five have been crossed: Biosphere integrity, climate change, chemical pollution, destruction of wild habitats and the nitrogen cycle are thought to have passed the safe threshold.
[283] The Gaia hypothesis, developed in the mid-20th century, compared Earth's environments and life as a single self-regulating organism leading to broad stabilization of the conditions of habitability.
[284][285][286] Images of Earth taken from space, particularly during the Apollo program, have been credited with altering the way that people viewed the planet that they lived on, called the overview effect, emphasizing its beauty, uniqueness and apparent fragility.