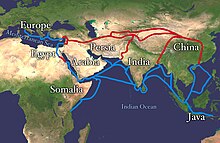
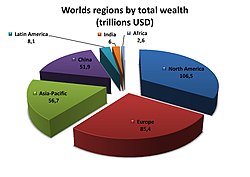
Economy of Asia
The largest economies in Asia in terms of PPP gross domestic product (GDP) are China, India, Japan, Taiwan, Indonesia, Turkey, South Korea, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Thailand, and Pakistan, Bangladesh and in terms of nominal gross domestic product (GDP) are Japan,Taiwan, South Korea, China, India, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Bangladesh, Thailand and Iran.
China (manufacturing and FDI-led growth[15]) and India (commodities, outsourcing destination and computer software) are the two fastest growing major economies in the world.
Close cooperation between the government, corporations and banks facilitated easy access to much-needed capital, and large conglomerates known as keiretsu spurred horizontal and vertical integration across all industries, keeping out foreign competition.
In addition to creating a conducive economic and political climate, the government developed the skills of its multi-racial workforce, and established export-oriented industries by encouraging foreign investors to set up regional operations in manufacturing.
For a short time, GDP contracted among nations such as Indonesia and Sri Lanka, despite massive inflow of foreign aid in the aftermath of the disaster.
[52] The financial crisis of 2007–2008, triggered by the housing bubble in the United States, caused a significant decline in the GDP of the majority of the European economies.
[53] The Arab Spring and the ensuing civil unrests since 2011 had caused economic malaise in Syria, Lebanon and Yemen, amongst the most adversely affected nations in the Middle East.
At the same time, in the early 2010s, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait registered their highest GDP growths on record in the years that followed due to increased oil prices and further diversification of exports, as well as rising foreign exchange reserves.
Japan was also affected by the COVID-19 pandemic amidst its declining population and a stagnant economy since the 2011 Fukushima nuclear accident, with its postponed hosting of the Summer Olympics to 2021.
South Korea, Singapore, Qatar, the Philippines, Indonesia and India were also affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, further raising fears of a recession across the continent after a streak of stock market losses in the region amidst nationwide lockdown in India and continued school and work closures in China, effectively quarantining more than 2 billion people (a quarter of the world's current human population).
Given the enormous quantity of cheap labor in the region, particularly in China and India, where large workforces provide an economic advantage over other countries, the rising standard of living will eventually lead to a slow-down.
[67][68][69] Following a Third Plenum of the Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party in 2013 China revealed plans for several sweeping social and economic reforms.
More importantly, it provides, for the first time, a feasible, controllable and expandable channel to investors to invest in both Hong Kong and Mainland, in addition to current schemes including QDII, QFII, AND RDFII programs.
China's central administration will impose hard caps on local government borrowing in order to control financial risks from an explosive level.
Though governments has yet to solve a variety of politically difficult issues, such as liberalising labour laws and reducing agricultural subsidies along with corruptions and fiscal deficits to sustain the growth.
[citation needed] The Indian automotive industry is one of the largest in the world with an annual production of 21.48 million vehicles (mostly two wheelers and cars) in FY 2013–14.
But then in FY 2013–14 the growth rebounded to 6.9% and then in 2014–15 it rose to 7.3% as a result of the reforms put by the New Government which led to the economy becoming healthy again and the current account deficit coming in control.
Cities like Bangalore, Hyderabad rival the United States's Silicon Valley in innovation and technological advancement as more and more skilled, tech-savvy students and young professionals are entering the entrepreneurial world.
Following the global economic recession, the Prime Minister hoped to boost Japanese economy with "three arrows": massive fiscal stimulus, more aggressive monetary easing and structural reforms to make Japan more competitive.
[101][102][103][104] The current member countries of ASEAN are Myanmar (Burma), Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, Philippines, Malaysia, Brunei Darussalam, Singapore and Indonesia.
[110][111][112][113] The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership is a proposed free trade agreement (FTA) between the ten member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam) and the six states with which ASEAN has existing free trade agreements (Australia, China, India, Japan, South Korea and New Zealand).
[116] RCEP is viewed as an alternative to the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), a proposed trade agreement which includes several Asian and American nations but excludes China and India.
Although the initial intention was to create a free trade area covering all membership (which includes China, the United States and Australia, among others) this has failed to materialize.
[119] In 2014, APEC members committed to taking a concrete step towards greater regional economic integration by endorsing a roadmap for the Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific (FTAAP) to translate this vision into a reality.
The study will provide an analysis of potential economic and social benefits and costs, analyze the various pathways towards a Free Trade Area and identify challenges economies may face in realizing this goal.
The vast expanse of the former Soviet Union, particularly that of Russia, contains a huge variety of metals, such as gold, iron, lead, titanium, uranium, and zinc.
They include Sony, Toyota, Toshiba, and Honda from Japan, and Asus, Acer from Taiwan, Samsung, Hyundai, LG, and Kia from South Korea.
[137] Many developed-nation firms from Europe, North America, Japan, Taiwan and South Korea have significant operations in developing Asia to take advantage of the abundant supply of cheap labor.
[136] Asia's top ten important financial centers are located in Hong Kong, Singapore, Tokyo, Shanghai, Beijing, Dubai, Shenzhen, Osaka, Seoul and Mumbai.
The increase of numbers of international banks major huge corporations are trying to cut their annual company expense by changing BPO to AI (Artificial Intelligence).