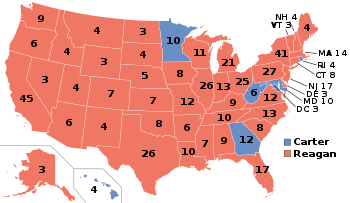
Electoral history of Ronald Reagan
Having been elected twice to the presidency,[1] Reagan reshaped the Republican Party, led the modern conservative movement, and altered the political dynamic of the United States.
[2] His 1980 presidential campaign stressed some of his fundamental principles: lower taxes to stimulate the economy,[3] less government interference in people's lives,[4] states' rights,[5] and a strong national defense.
[6] During his presidency, Reagan pursued policies that reflected his personal belief in individual freedom, brought changes domestically, both to the U.S. economy and expanded military, and contributed to the end of the Cold War.
[18] Despite an unsuccessful attempt to recall him in 1968,[24] Reagan was unopposed in the Republican primary[25] and was re-elected in 1970, defeating "Big Daddy" Jesse Unruh.
[35] Aided by the Iran hostage crisis and a worsening economy at home marked by high unemployment and inflation, Reagan won the election in a massive landslide.
[44] This was the second-most lopsided presidential election in modern U.S. history after Franklin D. Roosevelt's 1936 victory over Alfred M. Landon, in which he won 98.5 percent or 523 of the (then-total) 531 electoral votes.



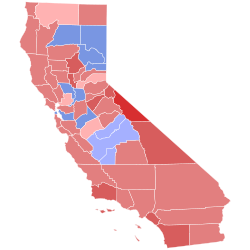

Red indicates a win by Reagan, blue a win by Ford.