Electricity sector in Japan
In the following years, most nuclear power plants have been on hold, being replaced mostly by coal and natural gas.
[3] Since the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster, and the subsequent large scale shutdown on the nuclear power industry, Japan's ten regional electricity operators have been making very large financial losses, larger than US$15 billion in both 2012 and 2013.
[8][9] In 2020 transmission and distribution infrastructure access will be made more open, which will help competitive suppliers cut costs.
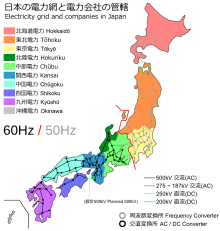
[8] Download coordinates as: Electricity transmission in Japan is unusual because the country is divided for historical reasons into two regions each running at a different mains frequency.
[10][11] Limitations of conversion capacity causes a bottleneck to transfer electricity and shift imbalances between the networks.
[10][11] Eastern Japan (consisting of Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto, and eastern parts of Chubu) runs at 50 Hz; Western Japan (including most of Chubu, Kansai, Chugoku, Shikoku, and Kyushu) runs at 60 Hz.
[15] The limitations of these links have been a major problem in providing power to the areas of Japan affected by the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster.
[13] During the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, there were blackouts in some areas of the country because of the insufficient ability of the three HVDC converter stations to transfer energy between both networks.
An energy white paper, approved by the Japanese Cabinet in October 2011, reported that "public confidence in safety of nuclear power was greatly damaged" by the Fukushima disaster, and it calls for a reduction in the nation's reliance on nuclear power.
[31] Carbon dioxide emissions from the electricity industry rose in 2012, reaching levels 39% more than when the reactors were in operation.
[37] The Japanese government announced in May 2011 a goal of producing 20% of the nation's electricity from renewable sources, including solar, wind, and biomass, by the early 2020s.
[38] In August 2011, the Japanese Government passed a bill to subsidize electricity from renewable energy sources.