Elliot Formation
The LEF is dominantly Late Triassic (Norian-Hettangian) in age while the UEF is mainly Early Jurassic (Sinemurian-Pliensbachian) and is tentatively regarded to preserve a continental record of the Triassic-Jurassic boundary in southern Africa.
Due to the reddish colour of the rocks, the Elliot Formation is colloquially referred to as the “Red Beds” in older geologic literature.
Common internal sedimentary structures of UEF sandstones are planar, low angle cross-bedding, horizontal and ripple-cross laminations.
The LEF was deposited in a fluvio-lacustrine environment where rivers were more perennial and formed meandering channel geometries, as evidenced by the presence of lateral accretion.
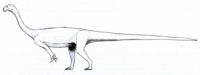
[15][16] Other species include Blikanasaurus cromptoni, Aardonyx celestae, Euskelosaurus browni, Antetonitrus ingenipes, Pulanesaura eocollum, and the largest sauropodomorph yet found, Ledumahadi mafube.
[17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24] Fossilised Massospondylus eggs, some with the fossilized remains of embryos intact, have been recovered from UEF deposits in the Golden Gate Highlands National Park.
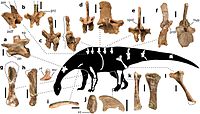
[34] Synapsids from the formation include the dicynodont Pentasaurus goggai[35] the tritheledontid cynodont Elliotherium kersteni[36][37] and the mammaliaform Megazostrodon rudnerae.