Emu Bay Shale
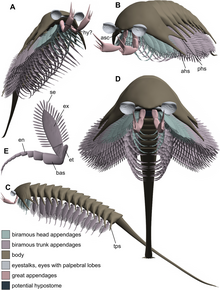
[3] More than 50 species of trilobites, non-biomineralized arthropods, palaeoscolecids, a lobopodian, a polychaete, vetulicolians, nectocaridids, hyoliths, brachiopods, sponges, chancelloriids, and a chelicerate are known from the Emu Bay Shale.
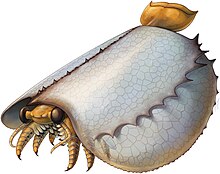
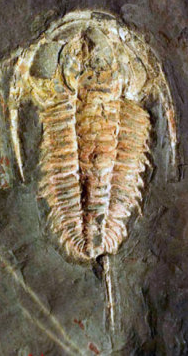
The site is also the source of high-quality specimens of trilobites such as Redlichia takooensis, Emuella polymera, Balcoracania dailyi, Megapharanaspis nedini, Holyoakia simpsoni, and Estaingia (=Hsuaspis) bilobata.
The Emu Bay Shale in contrast, appears to represent deposition in restricted basins on the inner shelf, indicating that soft tissue preservation occurred in a range of environmental settings during the Cambrian.
canadensis), Isoxys, Tuzoia, two species of the nektaspid arthropod Family Emucarididae (Emucaris fava and Kangacaris zhangi), the palaeoscolecid worm Wronascolex, the problematic Myoscolex and Vetustovermis, and a number of rarer elements.
NOTE: Much of the text of this article was used with permission of Sam Gon III from his below referenced web site, in particular from the Emu Bay page References about Australian trilobites: