Environment of Australia
The Australian environment ranges from virtually pristine Antarctic territory and rainforests to degraded industrial areas of major cities.
This dry and warm environment and exposure to cyclones, makes Australia particularly vulnerable to climate change -- with some areas already experiencing increases in wildfires and fragile ecosystems.
The island ecology of Australia has led to a number of unique endemic plant and animal species, notably marsupials like the kangaroo and koala.
The management of the impact on the environment from the mining industry, the protection of the Great Barrier Reef, forests and native animals are recurring issues of conservation.
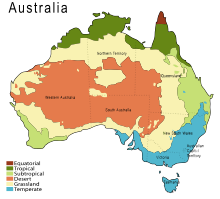
Although most of Australia is semi-arid or desert, it covers a diverse range of habitats, from alpine heaths to tropical rainforests, and is recognised as a megadiverse country.
Because of the great age and consequent low levels of fertility of the continent, its extremely variable weather patterns, and its long-term geographic isolation, much of Australia's biota is unique and diverse.
Australia has a rich variety of endemic legume species that thrive in nutrient-poor soils because of their symbiosis with Rhizobia bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi.
Issues such as climate change and global warming are expected to impact the supply of water in Australia in the future, which can lead to severe consequences such as prolonged droughts.
[14] In less urgent times, residents are still encouraged to conserve water and apply practices such as effluent reuse, rainwater harvesting and using greywater for various applicable purposes.
Larger scale projects in wastewater reclamation have been discussed in many major cities and successfully applied in Adelaide and Brisbane.
Increased coal mining in Australia is contentious because of the effects of global warming on Australia, emissions to air from coal burning power stations, dust, subsidence, impact on rivers like the Hunter River and other water users, failure to adequately restore mined areas, and lack of sustainability.
[citation needed] In urban areas, noise and odour are major sources of complaints to environmental protection authorities.
Australia is becoming hotter and more prone to extreme heat, bushfires, droughts, floods, and longer fire seasons because of climate change.
Average precipitation in the southwest and southeast Australia is projected to decline during this time, while regions such as the northwest may experience increases in rainfall.
[28] Furthermore, Australia's population is highly concentrated in coastal areas at risk from rising sea levels, and existing pressures on water supply will be exacerbated.
The exposure of Indigenous Australians to climate change impacts is exacerbated by existing socio-economic disadvantages which are linked to colonial and post-colonial marginalisation.
[29] Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander communities located in the coastal north are the most disadvantaged due to social and economic issues and their reliance on traditional land for food, culture, and health.
The SoE report provides a vital resource for policy makers, industry and NGOs, educational institutions, the science community and the general public.
[36] The southwest coastal area has a Mediterranean climate and was originally heavily forested, including large stands of the karri, one of the tallest trees in the world.
Thanks to the offshore Leeuwin Current, the area numbers in the top six regions for marine biodiversity, containing the most southerly coral reefs in the world.
[citation needed] The central four-fifths of the state are semiarid or desert and are lightly inhabited, with mining being the only significant activity.
Annual rainfall averages 200–250 millimetres (8–10 in), most of which occurs in sporadic torrential falls related to cyclone events in the summer months.
The Kimberley has a sweltering monsoonal climate with average annual rainfall ranging from 500 to 1,500 millimetres (20–60 in), but there is a very long, almost rainless season from April to November.
Still, the only development has occurred along the Ord River, restricted elsewhere due to violent floods and the insurmountable poverty of the generally shallow soils.