Incircle and excircles
In geometry, the incircle or inscribed circle of a triangle is the largest circle that can be contained in the triangle; it touches (is tangent to) the three sides.
[3] The center of the incircle, called the incenter, can be found as the intersection of the three internal angle bisectors.
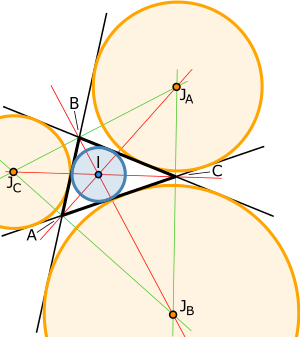
[3] Because the internal bisector of an angle is perpendicular to its external bisector, it follows that the center of the incircle together with the three excircle centers form an orthocentric system.
Because the incenter is the same distance from all sides of the triangle, the trilinear coordinates for the incenter are[6] The barycentric coordinates for a point in a triangle give weights such that the point is the weighted average of the triangle vertex positions.
are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, or equivalently (using the law of sines) by where
The weights are positive so the incenter lies inside the triangle as stated above.
The tangency points of the incircle divide the sides into segments of lengths
The distances from the incenter to the vertices combined with the lengths of the triangle sides obey the equation[9] Additionally,[10] where
The collection of triangle centers may be given the structure of a group under coordinate-wise multiplication of trilinear coordinates; in this group, the incenter forms the identity element.
[6] The distances from a vertex to the two nearest touchpoints are equal; for example:[11] If the altitudes from sides of lengths
is one-third of the harmonic mean of these altitudes; that is,[12] The product of the incircle radius
[15] The incircle radius is no greater than one-ninth the sum of the altitudes.
of the nine point circle is[17]: 232 The incenter lies in the medial triangle (whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides).
[17]: 233, Lemma 1 The radius of the incircle is related to the area of the triangle.
are the area, radius of the incircle, and semiperimeter of the original triangle, and
[22] Trilinear coordinates for the vertices of the intouch triangle are given by[citation needed] Trilinear coordinates for the Gergonne point are given by[citation needed] or, equivalently, by the Law of Sines, An excircle or escribed circle[2] of the triangle is a circle lying outside the triangle, tangent to one of its sides, and tangent to the extensions of the other two.
[3] The center of an excircle is the intersection of the internal bisector of one angle (at vertex
The center of this excircle is called the excenter relative to the vertex
[3] Because the internal bisector of an angle is perpendicular to its external bisector, it follows that the center of the incircle together with the three excircle centers form an orthocentric system.
, the excenters have trilinears[citation needed] The radii of the excircles are called the exradii.
as the radius of the incircle, By the Law of Cosines, we have Combining this with the identity
Trilinear coordinates for the vertices of the extouch triangle are given by[citation needed] Trilinear coordinates for the Nagel point are given by[citation needed] or, equivalently, by the Law of Sines, The Nagel point is the isotomic conjugate of the Gergonne point.
It is so named because it passes through nine significant concyclic points defined from the triangle.
These nine points are:[28][29] In 1822, Karl Feuerbach discovered that any triangle's nine-point circle is externally tangent to that triangle's three excircles and internally tangent to its incircle; this result is known as Feuerbach's theorem.
He proved that:[30] The triangle center at which the incircle and the nine-point circle touch is called the Feuerbach point.
The points of intersection of the interior angle bisectors of
Trilinear coordinates for the vertices of the incentral triangle
Its sides are on the external angle bisectors of the reference triangle (see figure at top of page).
The four circles described above are given equivalently by either of the two given equations:[31]: 210–215 Euler's theorem states that in a triangle: where
Among their many properties perhaps the most important is that their two pairs of opposite sides have equal sums.