Extraterrestrial atmosphere
The enormous amount of CO2 in the atmosphere creates a strong greenhouse effect, raising the surface temperature to around 470 °C, hotter than that of any other planet in the Solar System.
"[9] The Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, though spanning a much shorter dataset, shows no warming of planetary average temperature, and a possible cooling.
[17] On June 7, 2018, NASA announced that the Curiosity rover detected a cyclical seasonal variation in atmospheric methane, as well as the presence of kerogen and other complex organic compounds.
The best-known feature of the cloud layer is the Great Red Spot, a persistent anticyclonic storm located 22° south of the equator that is larger than Earth.
In 2000, an atmospheric feature formed in the southern hemisphere that is similar in appearance to the Great Red Spot, but smaller in size.
[26][27] This is hypothesized to be part of an approximately 70 year global climate cycle, characterized by the relatively rapid forming and subsequent slow erosion and merging of cyclonic and anticyclonic vortices in Jupiter's atmosphere.
However, the storms and the band pattern are less visible and active than those of Jupiter, due to the overlying ammonia hazes in Saturn's troposphere.
Like Jupiter and Saturn, Uranus has a banded cloud layer, although this is not readily visible without enhancement of visual images of the planet.
[citation needed] Images taken in 1997 with the Hubble Space Telescope showed storm activity in that part of the atmosphere emerging from the 25-year-long Uranian winter.
[32] Ten of the many natural satellites in the Solar System are known to have atmospheres: Europa, Io, Callisto, Enceladus, Ganymede, Titan, Rhea, Dione, Triton and Earth's Moon.
The atmosphere of Enceladus is also extremely thin and variable, consisting mainly of water vapor, nitrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide vented from the moon's interior through cryovolcanism.
The hydrocarbons are thought to form in Titan's upper atmosphere in reactions resulting from the breakup of methane by the Sun's ultraviolet light, producing a thick orange smog.
The haze that can be seen in the adjacent picture contributes to the moon's anti-greenhouse effect and lowers the temperature by reflecting sunlight away from the satellite.
Elliot and his colleagues believe that Triton's warming trend could be driven by seasonal changes in the absorption of solar energy by its polar ice caps.
[36] Bonnie J. Buratti et al. argue the changes in temperature are a result of deposition of dark, red material from geological processes on the moon, such as massive venting.
[37] Pluto has an extremely thin atmosphere that consists of nitrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide, derived from the ices on its surface.
[38] Two models[39][40] show that the atmosphere does not completely freeze and collapse when Pluto moves further from the Sun on its extremely elliptical orbit.
Observations of a second occultation on August 20, 2002 suggest that Pluto's atmospheric pressure has tripled, indicating a warming of about 2 °C (3.6 °F),[41][42] as predicted by Hansen and Paige.
[44] One astronomer has speculated the warming may be a result of eruptive activity, but it is more likely Pluto's temperature is heavily influenced by its elliptical orbit.
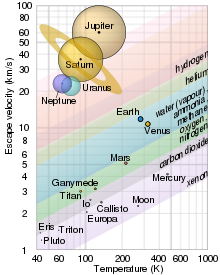
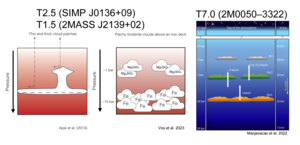
[46] Brown dwarfs have an atmosphere that produces a spectrum from late M-type, over L-type, T-type and finally arriving at Y-dwarf with decreasing temperature.
Later observations with the Hubble Space Telescope showed an enormous ellipsoidal envelope of hydrogen, carbon and oxygen around the planet.
[74] The presence of molecular oxygen (O2) may be detectable by ground-based telescopes,[75] and it can be produced by geophysical processes, as well as a byproduct of photosynthesis by life forms, so although encouraging, O2 is not a reliable biosignature.
Ozone and hydrocarbons absorb large amounts of ultraviolet radiation, heating the upper parts of atmospheres that contain them, creating a temperature inversion and a stratosphere.
A temperature inversion, and stratosphere was identified on WASP-33b caused by titanium oxide, which is a strong absorber of visible and ultraviolet radiation, and can only exist as a gas in a hot atmosphere.
[82] In September 2019, two independent research studies concluded, from Hubble Space Telescope data, that there were significant amounts of water in the atmosphere of exoplanet K2-18b, the first such discovery for a planet within a star's habitable zone.
[50][51] High altitude clouds often block light coming from deeper layers of the atmosphere, including chemical absorption features.
[103] A newer type of exoplanets, called ultra-hot Jupiters have a temperature above 2,000 K and have a cloud-free dayside[100] with molecules often dissociated into atoms or ions.
The photolysis of water (H2O) by UV rays followed by hydrodynamic escape of hydrogen can lead to a build-up of oxygen in planets close to their star undergoing runaway greenhouse effect.
In the absence of such gases, the likelihood of build-up of oxygen also depends in complex ways on the planet's accretion history, internal chemistry, atmospheric dynamics, and orbital state.
[113] The ratio of nitrogen and argon to oxygen could be detected by studying thermal phase curves[114] or by transit transmission spectroscopy measurement of the spectral Rayleigh scattering slope in a clear-sky (i.e. aerosol-free) atmosphere.