Textile
[4] In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns.
[4][6] The durability of textiles is an important property, with common cotton or blend garments (such as t-shirts) able to last twenty years or more with regular use and care.
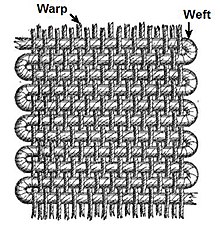
[9] Yarns are then used to make different kinds of fabric by weaving, knitting, crocheting, knotting, tatting, or braiding.
[10][11][5] After manufacturing, textile materials are processed and finished to add value, such as aesthetics, physical characteristics, and increased usefulness.
[14] The word 'textile' comes from the Latin adjective textilis, meaning 'woven', which itself stems from textus, the past participle of the verb texere, 'to weave'.
[9][16][3] A "fabric" is defined as any thin, flexible material made from yarn, directly from fibers, polymeric film, foam, or any combination of these techniques.
Stemming most recently from the Middle French fabrique, or "building," and earlier from the Latin fabrica ('workshop; an art, trade; a skillful production, structure, fabric'), the noun fabrica stems from the Latin faber" artisan who works in hard materials', which itself is derived from the Proto-Indo-European dhabh-, meaning 'to fit together'.
[19] Cloth is a flexible substance typically created through the processes of weaving, felting, or knitting using natural or synthetic materials.
[23] The Banton Burial Cloth, the oldest existing example of warp ikat in Southeast Asia, is displayed at the National Museum of the Philippines.
The first clothes, worn at least 70,000 years ago and perhaps much earlier, were probably made of animal skins and helped protect early humans from the elements.
The discovery of dyed flax fibers in a cave in the Republic of Georgia dated to 34,000 BCE suggests that textile-like materials were made as early as the Paleolithic era.
A textile is any material made of interlacing fibers, including carpeting and geotextiles, which may not necessarily be used in the production of further goods, such as clothing and upholstery.
In the household, textiles are used in carpeting, upholstered furnishings, window shades, towels, coverings for tables, beds, and other flat surfaces, and in art.
Threads coated with zinc oxide nanowires, when woven into fabric, have been shown capable of "self-powering nanosystems", using vibrations created by everyday actions like wind or body movements to generate energy.
Aesthetics, durability, comfort and safety, appearance retention, care, environmental impact, and cost are the serviceability concepts employed in structuring the material.
Appliqué work of pipili is decorative art of Odisha, a state in eastern India, used for umbrellas, wall hangings, lamp shades, and bags.
[clarification needed] After a modest drop due to COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, global fiber output rebounded to 113 million tons in 2021.
Reasons include its low price, the demand-supply imbalance of cotton, and its [Synthetic fibers'] versatility in design and application.
[clarification needed] Bacterial cellulose can be made from industrial organic and agricultural waste, and used as material for textiles and clothing.
It was developed by Joseph Marie Jacquard based on earlier inventions by Basile Bouchon (1725), Jean Baptiste Falcon (1728), and Jacques Vaucanson (1740).
The competitive advantages of the China are low prices and abundant labor, lowered commercial obstacles, and a ready supply of raw materials.
[130][131] China's apparel market share has declined in recent years due to various reasons and a shift toward high-end, sophisticated products.
Since the 1990s, with advances in technologies such as permanent press process, finishing agents have been used to strengthen fabrics and make them wrinkle free.
[137] More recently, nanomaterials research has led to additional advancements, with companies such as Nano-Tex and NanoHorizons developing permanent treatments based on metallic nanoparticles for making textiles more resistant to things such as water, stains, wrinkles, and pathogens such as bacteria and fungi.
Water pollution generated by the discharge of untreated wastewater and the use of toxic chemicals, particularly during processing, account for the majority of the global environmental concerns linked with the textile industry.
However, the discharge of untreated effluents into water bodies is responsible for the majority of environmental harm produced by the textile sector.
[151] The textile sector is believed to use 79 trillion litres of water per year and to discharge around 20% of all industrial effluent into the environment.
[152] Reportedly, aromatic and heterocyclic compounds with color-display and polar groups make up most of the dyes used in textile coloration processes.
In 2023, North Carolina State University researchers used enzymes to separate cotton from polyester in an early step towards reducing textile waste, allowing each material to be recycled.
The law prohibits misinformation about the fiber content, misbranding, and any unfair advertising practice, as well as requires businesses to operate in a particular manner.