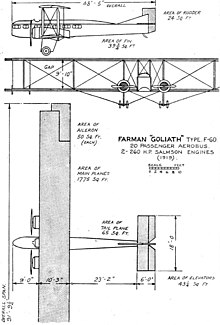
Farman F.60 Goliath
The Goliath was initially designed in 1918 as a heavy bomber capable of carrying 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) of bombs with a range of 1,500 km (930 mi).
Nonetheless he was quick to understand that the big, box-like fuselage of the Goliath could be easily modified to convert the aircraft into an airliner.
Since non-military flying was not permitted at that date, Lucien Bossoutrot and his passengers were all ex-military pilots who wore uniforms and carried mission orders for the circumstances.
In 1920, the Compagnie des Grands Express Aériens (CGEA) began scheduling regular flights between Le Bourget and Croydon.
The Société Générale de Transports Aériens (SGTA) opened a Paris-Brussels route in July 1920, flown by the Goliath.
The Belgian airline Société Nationale pour l'Etude des Transports Aériens (SNETA) also opened a Brussels-London route in April 1921.