Francesco di Giorgio Martini
In panels painted for cassoni he departed from the traditional representations of joyful wedding processions in frieze-like formulas to express visions of ideal, symmetrical, vast and all but empty urban spaces rendered in perspective.
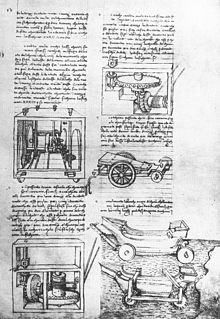
He composed an architectural treatise Trattato di architettura, ingegneria e arte militare, the third of the Quattrocento, after Leone Battista Alberti's and Filarete's; he worked on it for decades and finished sometime after 1482; it circulated in manuscript.
[2][3] The treatise was included in several original manuscripts with one copy (i.e., Codex Mediceo Laurenziano 361) belonged to Leonardo da Vinci who had made notes and sketches within.
Francesco di Giorgio's painting of the "Madonna and Child with 2 Angels" is found at the Lowe Art Museum in Coral Gables, Florida.
[7] During this period, Francesco di Giorgio was also working with assistants on The Coronation of the Virgin for the Santa Maria della Scala (Siena), a large painted altarpiece.
[7] Architectural work also came to Di Giorgio through his employment with the Duke, including what is probably his most famous building, Santa Maria delle Grazie al Calcinaio in Cortona.
Letters from 1485 reveal that the Sienese government wrote to Francesco di Giorgio to request that he return to his native city and embark on the design and construction of public buildings.
[7] Di Giorgio also completed artistic projects for the city, such as the candle-holding angel sculptures which he contributed to the altar at the Opera del Duomo.