Electric discharge in gases
The breakdown voltage for the glow discharge depends nonlinearly on the product of gas pressure and electrode distance according to Paschen's law.
A small amount of a radioactive element may be added into the tube, either as a separate piece of material (e.g. nickel-63 in krytrons) or as addition to the alloy of the electrodes (e.g. thorium), to preionize the gas and increase the reliability of electrical breakdown and glow or arc discharge ignition.
[2] The E/N ratio between the electric field E and the concentration of neutral particles N is often used, because the mean energy of electrons (and therefore many other properties of discharge) is a function of E/N.
[3] According to a Nature news article describing the work,[4] researchers at Imperial College London demonstrated how they built a mini-map that gives tourists luminous route indicators.
To make the one-inch London chip, the team etched a plan of the city centre on a glass slide.


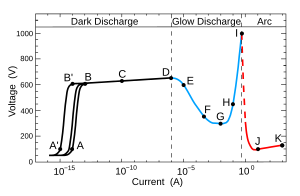
A: random pulses by cosmic radiation
B: saturation current
C: avalanche Townsend discharge
D: self-sustained Townsend discharge
E: unstable region: corona discharge
F: sub-normal glow discharge
G: normal glow discharge
H: abnormal glow discharge
I: unstable region: glow-arc transition
J: electric arc
K: electric arc
The A-D region is called a dark discharge; there is some ionization, but the current is below 10 microamperes and there is no significant amount of radiation produced.
The F-H region is a region of glow discharge; the plasma emits a faint glow that occupies almost all the volume of the tube; most of the light is emitted by excited neutral atoms.
The I-K region is a region of arc discharge; the plasma is concentrated in a narrow channel along the center of the tube; a great amount of radiation is produced.