Genetically modified food
Genes encoded for desired features, for instance an improved nutrient level, pesticide and herbicide resistances, and the possession of therapeutic substances, are often extracted and transferred to the target organisms, providing them with superior survival and production capacity.
"[44] What constitutes a genetically modified organism (GMO) is not clear and varies widely between countries, international bodies and other communities, has changed significantly over time, and was subject to numerous exceptions based on "convention", such as exclusion of mutation breeding from the EU definition.
[97] Geographically though the spread has been uneven, with strong growth in the Americas and parts of Asia and little in Europe and Africa[91] in 2013 only 10% of world cropland was GM, with the US, Canada, Brazil, and Argentina being 90% of that.
[99][100][101] Long before humans began using transgenics, sweet potato emerged naturally 8000 years ago by embedding of genes from bacteria, that increased its sugar content.
According to Del Monte's submission, the pineapples are commercially grown in a "monoculture" that prevents seed production, as the plant's flowers aren't exposed to compatible pollen sources.
[130] It is intended to produce a fortified food to be grown and consumed in areas with a shortage of dietary vitamin A,[131] a deficiency which each year is estimated to kill 670,000 children under the age of 5[132] and cause an additional 500,000 cases of irreversible childhood blindness.
[136][137][138] In April 2016, a white button mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) modified using the CRISPR technique received de facto approval in the United States, after the USDA said it would not have to go through the agency's regulatory process.
GM beets are approved for import and consumption in Australia, Canada, Colombia, EU, Japan, Korea, Mexico, New Zealand, Philippines, the Russian Federation and Singapore.
Genetic engineering made it possible to extract rennet-producing genes from animal stomachs and insert them into bacteria, fungi or yeasts to make them produce chymosin, the key enzyme.
[187] Genetically modified foods are usually edited to have some desired characteristics, including certain benefits for surviving extreme environments, an enhanced level to nutrition, the access of therapeutic substances, and the resistance genes to pesticide and herbicides.
[10] Foods are well monitored to gain specific qualities that became practical, for example, concentrated nutraceutical levels and health-promoting chemicals, making them a desirable component of a varied diet.
[188] Among the notable breakthroughs of genetic modification is Golden Rice, whose genome is altered by the injection of the vitamin A gene from a daffodil plant conditioning provitamin A production.
[10] In addition, increased mineral, vitamin A, and protein content has played a critical role in preventing childhood blindness and iron deficiency anemia.
[15] Scientific evidence has shown that inadequate consumption of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids is generally associated with the development of chronic diseases and developmental aberrations.
[12][14][15] The genetically modified organisms, including potato, tomato, and spinach are applied in the production of substances that stimulate the immune system to respond to specific pathogens.
The transgenic organisms are usually applied to use as oral vaccines, which allows the active substances to enter the human digestive system, targeting the alimentary tract in which stimulate a mucosal immune response.
[15] Additionally, transgenic plants are widely used as bioreactors in the production of pharmaceutical proteins and peptides, including vaccines, hormones, human serum albumin (HSA), etc.
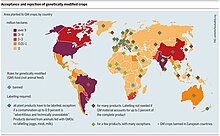
[32][33][34][35] The legal and regulatory status of GM foods varies by country, with some nations banning or restricting them, and others permitting them with widely differing degrees of regulation.
[197] If new substances are found, further testing may be required to satisfy concerns over potential toxicity, allergenicity, possible gene transfer to humans or genetic outcrossing to other organisms.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is responsible for monitoring pesticide usage, including plants modified to contain proteins toxic to insects.
However, the value of human dignity, liberty, equality, and solidarity, as well as the status of democracy and law, as emphasized in the European Charter of Fundamental Rights, are considered the ethical framework governing the employment of scientific and technological research and development.
[211] At the same time, due to lack of single, clear definition of GMO, a number of foods created using genetic engineering techniques (such as mutation breeding) are excluded from labelling and regulation based on "convention" and traditional usage.
The real-time PCR assays using specific probes confirmed all the results and proved that it is possible to detect and quantify genetically modified organisms in the fully refined soybean oil.
[citation needed] "GMO-free" labelling schemes are causing controversies in farming community due to lack of clear definition, inconsistency of their application and are described as "deceptive".
[10][223] In vitro assays such as RAST or serum from people allergic to the original crop could be applied to test the allergenicity of GM goods with known source of the gene.
[226] The Bt genes are usually obtained from the soil bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis, and they can generate a protein that breaks down in the insect’s gut, releasing a toxin called delta-endotoxin, which causes paralysis and death.
[11] An international database that demonstrated genetic contaminations with undesired seeds has been a major problem due to the expansion of field trials and commercially viable cultivation of GM crops around the world.
[228] Another crucial link of the change in consumer attitudes towards genetically modified foods has been shown to be closely related to their interaction with socioeconomic and demographic characteristics, for example, age, ethnicity, residence, and level of consumption.
[11][222][229] On the one hand, it was found that consumers in most European countries, especially in northern Europe, the UK and Germany, believe that the benefits of GM foods do not outweigh the potential risks.
Here, we show that a number of articles some of which have strongly and negatively influenced the public opinion on GM crops and even provoked political actions, such as GMO embargo, share common flaws in the statistical evaluation of the data.