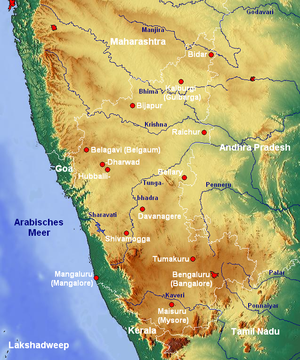
Geography of Karnataka
The Indian State of Karnataka is located between 11°30' North and 18°30' North latitudes and between 74° East and 78°30' East longitude.It is situated on a tableland where the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats converge into the complex, in the western part of the Deccan Peninsular region of India.
The highest point in Karnataka is the Mullayanagiri hill in Chikkamagaluru district which has an altitude of 1,929 metres (6,329 ft) above sea level.
Rich deposits of asbestos, bauxite, chromite, dolomite, gold, iron ore, kaolin, limestone, magnesite, Manganese, ochre, quartz, and silica sand are found in the state.
Karnataka has very rich deposits of high-grade iron and manganese ores to the tune of 1,000 million tonnes.
Entisols, Inceptisols, Mollisols, Spodosols, Alfisols, Ultisols, Oxisols, Aridisols, Vertisols, Andisols and Histosols.
The next three months (July, August and September) are somewhat comfortable due to reduced day temperature although the humidity continue to be very high.
[7] Karnataka is divided into three meteorological zones: The southwest monsoon accounts for almost 80% of the rainfall that the state receives.
The following were the top 5 places that peaked in rainfall statistics [2010-2017] [10][11][12][13] About 38724 km² (or 20% of Karnataka's geographic) are covered by forests.