Global Energy and Water Exchanges
GEWEX is a collaboration of researchers worldwide to find better ways of studying the water cycle and how it transforms energy through the atmosphere.
IGPO oversees major initiatives and coordinates between national projects in an effort to bring about communication between researchers.
[4] The Scientific Steering Group organizes the projects and assigns them to panels, which oversee progress and provide critique.
[8] This ignored the large amount of weather that occurs over the oceans and unpopulated regions, with key data missing from these areas.
Since satellites orbiting the Earth cover large areas in small time frames, they can better estimate climate where measurements are infrequently taken.
When the air reaches land, which may be warmer, there may be inadequate convection and other processes to create rains, and this can cause droughts.
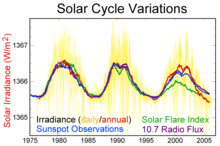
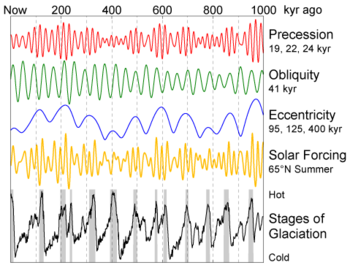
[12] Aside from fluctuations of solar radiation, the sunlight that is transformed by the Earth can vary greatly, some have concluded for instance, that ice-ages self-perpetuate once enough ice has accumulated in the polar regions to reflect enough radiation at high elevations to lower the global average temperature, whereas it takes an unusually warm period to reverse this state.
The experiment takes a sampling of climate, with some trends lasting a million years, and as paleo-climatology shows, can abruptly change.
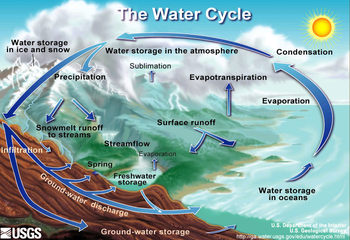
GEWEX was also designed to model the global hydrological cycle and its impact on the atmosphere, oceans and land surfaces.
It was also to advance the development of observing techniques, data management, and assimilation systems for operational application to long-range weather forecasts, hydrology, and climate predictions.
CEOP projects interacted with other non-GEWEX projects like CLIVAR and CLiC The results of the build-up phase include 15 to 25 years of study, measured the indirect effects of aerosols, compiled a correlated data set, some reductions in uncertainty[18] GEWEX claims the following accomplishments: A long period data set of clouds, rain fall, water vapor, surface radiation, and aerosols with no indication of large global trends, but with evidence of regional variability, models showing increased precipitation, and showed the importance of regional factors, such as water and soil conservation in regional climate change.
The coordination between ground sensing observations and satellite information allowed a more thorough analysis of events that led up to the flood.
Researchers at the Center for Ocean-Land-Atmosphere Studies (COLA) found that upstream soil moisture and a multifold increase of moist air flow from the Gulf of Mexico to the flooded regions was a major factor in excessive rainfall.
The number of ground sensing stations (currently around 40) in the BSRN is rather limited for global observation this affected the measurement of aerosols which are regionally dominant.
[18] Currently scientist use NASA Aqua's Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer (AMSR-E) to evaluation soil moisture from space.
There are several regional project areas most of these are now covered by CEOP For CEOP which survey the hydroclimate for southern African (AMMA), Baltic Sea area (BALTEX), North America (CPPA), Eastern Amazonia (LBA), La Plate Basin (LBB), Asia (MAHASRI), Australia (MDB), and Northern Eurasia (NEEPSI).
Fourth, to collaborate with other hydrological science projects to create tools for assessing the water-system consequences of predictions and global climate change.
GPCP task was to estimate precipitation using satellites that were global including places where people were not present to take measurements.
As the study period of the project increased past 25 years a third objective was added analyze long-term variation, such as that caused by global warming.
Also, in a renewed effort for better data and with more observation satellites, the GPCP, hopes to gain insights to rainfall variation on 'weather'-scale, or 4-hour periods to daily time scales.
[27] Established by Radiation Sciences Program(NASA) and GEWEX in 1998 to analyze satellite and field data to determine the distribution of aerosols, how they are formed, transformed and transported.
[29] The GEWEX modelling and prediction panel (GMPP) is charged with the task of finding better ways to use the data by other projects and other agencies.
[32] In addition, in other parts of the GEWEX study, these oscillations are an aspect of climate forcing, which allow testing of predictions and models.
This modelling may be complicated by the fact that the North Atlantic Oscillation in switching state (see graph) as the effects of global warming are becoming more prominent.
In 2008, sea ice extent decline has backed off from the previous years' trend, and researchers had forecast a strong La Nina event for late 2007 and 2008.
When multiple climate-forcing influences are acting simultaneously in which one of the events will eventually take dominance, lack of precedents from the past study of similar confluences of events, as well as knowledge of the uncertainty of sensitive 'switches' in the oceanic/atmospheric switches may affect the ability to provide accurate models and predictions.
A thermocline is a sharp temperature drop at depth; it varies during the year, with location, and over long periods of time.
The Pacific Decadal Anomaly (PDA See image) may influence the source, direction or momentum of rise of the cold water component of the thermocline.
Such a stalling of long-term cycles is believed to be a factor in the Dryas period, a warming interrupted by surface impacts of extraterrestrial origin may have occurred over hundreds of years.
Reductions of glacial ice on land masses can cause isostatic rebounds and may affect earthquakes and volcanism over a wide range.