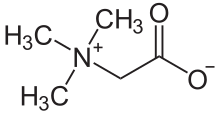
Trimethylglycine
Betaine, sold under the brand name Cystadane is indicated for the adjunctive treatment of homocystinuria, involving deficiencies or defects in cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS), 5,10-methylene-tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR), or cobalamin cofactor metabolism (cbl).
It serves as a appetitive attractant to generalist carnivores such as the predatory sea slug Pleurobranchaea californica.
One step in the methylation cycle is the remethylation of homocysteine, a compound which is naturally generated during demethylation of the essential amino acid methionine.
Despite its natural formation, homocysteine has been linked to inflammation, depression, specific forms of dementia, and various types of vascular disease.
The second pathway (restricted to liver and kidney in most mammals) involves betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase (BHMT) and requires trimethylglycine as a cofactor.
[14] Further degradation of betaine, via the enzyme dimethylglycine dehydrogenase produces folate, thus contributing back to methionine synthase.
[17] The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved betaine trimethylglycine (also known by the brand name Cystadane) for the treatment of homocystinuria, a disease caused by abnormally high homocysteine levels at birth.
[24] Although rare, it can also causes excessive increases in serum methionine concentrations in the brain, which may lead to cerebral edema, a life-threatening condition.
[24] Trimethylglycine supplementation lowers homocysteine but also raises (given in high doses of 6g/day) LDL-cholesterol in obese individuals and renal patients.