Sustainable architecture
Going beyond the technical sphere of "green design", invention and expertise, some scholars are starting to position architecture within a much broader cultural framework of the human interrelationship with nature.
Adopting this framework allows tracing a rich history of cultural debates about humanity's relationship to nature and the environment, from the point of view of different historical and geographical contexts.
[10] Site analysis can be employed to optimize use of local environmental resources such as daylight and ambient wind for heating and ventilation.
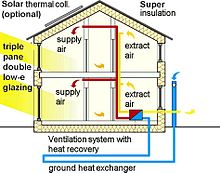
[12] An important and cost-effective element of an efficient heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system is a well-insulated building.
In colder climates, heating systems are a primary focus for sustainable architecture because they are typically one of the largest single energy drains in buildings.
Masonry building materials with high thermal mass are very valuable for retaining the cool temperatures of night throughout the day.
In addition builders often opt for sprawling single story structures in order to maximize surface area and heat loss.
Small-scale rooftop wind turbines have been known to be able to generate power from 10% to up to 25% of the electricity required of a regular domestic household dwelling.
Unanticipated breakdowns can have a significant impact on a project's profitability due to the logistical and practical difficulties of replacing critical components in a wind turbine.
Uncertainty with the long-term component reliability has a direct impact on the amount of confidence associated with cost of energy (COE) estimates.
The up-front cost of installing solar collectors is high, but with the annual energy savings, payback periods are relatively short.
[27] A 2022 study surrounding projected emission decreases within Sweden’s Kymenlaakso region explored the aspect of retrofitting existing apartment buildings (of varying ages) with EAHP systems.
Select buildings were chosen in the cities of Kotka and Kouvola, their projected carbon emissions decreasing by about 590 tCO2 and 944 tCO2 respectively with a 7 - 13 year payoff period.
[28] It is, however, important to note that EAHP systems may not produce favourable results if installed in a building exhibiting incompatible exhaust output rates or electricity consumption.
Ground-source takes advantage of the relatively constant, mild temperatures underground, which means their efficiencies can be much greater than that of an air-source heat pump.
"[35] Some examples of sustainable building materials include recycled denim or blown-in fiber glass insulation, sustainably harvested wood, Trass, Linoleum,[36] sheep wool, hempcrete, roman concrete,[37] panels made from paper flakes, baked earth, rammed earth, clay, vermiculite, flax linen, sisal, seagrass, expanded clay grains, coconut, wood fiber plates, calcium sandstone, locally obtained stone and rock, and bamboo, which is one of the strongest and fastest growing woody plants, and non-toxic low-VOC glues and paints.
[40] Regenerative sources, use of waste material, and the ability to reuse are sustainable qualities of timber, thatching, and stone and clay.
VOCs have a high vapor pressure and low water solubility, and are suspected of causing sick building syndrome type symptoms.
As of October 2022, researchers at MIT have made developments on lab-grown Zinnia elegans cells growing into specific characteristics under conditions within their control.
[46] David N. Bengston from the USDA suggests that this alternative would be more efficient than traditional wood harvesting, with future developments potentially saving on transportation energy and conserve forests.
However, Bengston notes that this breakthrough would change paradigms and raises new economic and environmental questions, such as timber-dependent communities′ jobs or how conservation would impact wildfires.
There is little coherence in the measurement and assessment of materials sustainability attributes, resulting in a landscape today that is littered with hundreds of competing, inconsistent and often imprecise eco-labels, standards and certifications.
This discord has led both to confusion among consumers and commercial purchasers and to the incorporation of inconsistent sustainability criteria in larger building certification programs such as LEED.
BIM services, including conceptual and topographic modelling, offer a new channel to green building with successive and immediate availability of internally coherent, and trustworthy project information.
Ideally, most building should avoid suburban sprawl in favor of the kind of light urban development articulated by the New Urbanist movement.
[53] Careful mixed use zoning can make commercial, residential, and light industrial areas more accessible for those traveling by foot, bicycle, or public transit, as proposed in the Principles of Intelligent Urbanism.
The study of permaculture, in its holistic application, can also greatly help in proper building placement that minimizes energy consumption and works with the surroundings rather than against them, especially in rural and forested zones.
[60] Waste takes the form of spent or useless materials generated from households and businesses, construction and demolition processes, and manufacturing and agricultural industries.
These materials are loosely categorized as municipal solid waste, construction and demolition (C&D) debris, and industrial or agricultural by-products.
[61] Sustainable architecture focuses on the on-site use of waste management, incorporating things such as grey water systems for use on garden beds, and composting toilets to reduce sewage.