Guadiana
After the Muslim conquest of the Iberian Peninsula, the name was extended and referred to as Wadi Ana, later passed on to Portuguese and Spanish settlers as the Ouadiana, and later just Odiana.
Since the 16th century, the name slowly evolved to take on the form Guadiana, a cognitive variation that developed from many Andalusi river place-names beginning in wadi using the prefix guad- such as the hydronyms Guadalquivir, Guadalete, and Guadarrama.
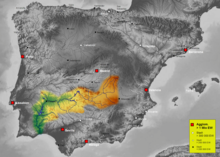
From its origin/spring runs from the southern Iberian plain in a direction east to west, to near the town of Badajoz, where it begins to track south leading to the Gulf of Cádiz.
The ecosystem has Mediterranean hydrological characteristics, including high variation in intra- and inter-annual discharge, large floods and severe droughts.
[7] The river empties into the Gulf of Cádiz between Ayamonte and Vila Real de Santo António, the two highly touristic regions of the Algarve and the sea-side of Andalusia.
Tides are semi-diurnal, ranging from 0.8 to 3.5 metres (2.6 to 11.5 ft); their upriver propagation is limited by falls situated 76 kilometres (47 mi) from the mouth at Moinho dos Canais.
In Spain, three autonomous communities, (Castilla-La Mancha, Extremadura and Andalusia) (comprising the provinces of Ciudad Real, Badajoz, and Huelva) are crossed by the Guadiana.