Gun violence in the United States
Gun violence is a term of political, economic and sociological interest referring to the tens of thousands of annual firearms-related deaths and injuries occurring in the United States.
[50][51] Further studies by HICRC found the following: firearms in the home are used more often to intimidate intimates than to thwart crime;[52] gun use in self-defense is rare and not more effective at preventing injury than other protective actions;[53] and a study of hospital gun-shot appearances does not back up the claim of millions of defensive gun use, as virtually all criminals with a gunshot wound go to hospital;[54][55] with virtually all having been shot whilst the victim of crime and not shot whilst offending.
[69] Using cross-sectional time-series data for U.S. counties from 1977 to 1992, Lott and Mustard of the Law School at the University of Chicago found that allowing citizens to carry concealed weapons deters violent crimes and appears to produce no increase in accidental deaths.
[101] Gun-related deaths among children in the U.S. in 2021 was 4,752, surpassing the record total seen during the first year of the pandemic, a new analysis of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data found.
Ultimately, when study participants were provoked, their reaction was substantially more aggressive when a gun was visibly present in the room, in contrast with a more benign object like a tennis racket.
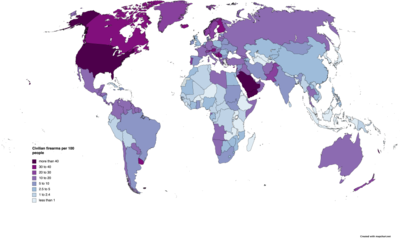
[150] Canada and Switzerland each have much looser gun control regulation than the majority of developed nations, although significantly more than in the United States, and have firearm death rates of 2.22 and 2.91 per 100,000 citizens, respectively.
[9] A study conducted by the Journal of the American Medical Association determined that worldwide yearly gun deaths had reached 250,000 by 2018 and that the United States was one of only six countries that collectively accounted for roughly half of those fatalities.
[185] Between January 1 and May 18, 2018, 31 students and teachers were killed inside U.S. schools, exceeding the number of U.S. military service members who died in combat and noncombat roles during the same period.
Across different studies conducted, it has been found that US public opinion varies based on gender, age, gun ownership status, occupation, education, political affiliation among many other demographics.
[229] In the midst of a recent surge in mass shootings, including a record 46 school shootings in 2022, an April 2023 Fox News poll found registered voters overwhelmingly supported a wide variety of gun restrictions: Public policy as related to preventing gun violence is an ongoing political and social debate regarding both the restriction and availability of firearms within the United States.
[233] At the federal, state and local level, gun laws such as handgun bans have been overturned by the Supreme Court in cases such as District of Columbia v. Heller and McDonald v. Chicago.
[246] A 2018 study determined that California's implementation of comprehensive background checks and misdemeanor violation policies was not associated with a net change in the firearm homicide rate over the ensuing 10 years.
The Act also prohibited sale of firearms to felons, those under indictment, fugitives, illegal aliens, drug users, those dishonorably discharged from the military, and those in mental institutions.
"[278] The Violent Crime Control and Law Enforcement Act, enacted in 1994, included the Federal Assault Weapons Ban, and was a response to public fears over mass shootings.
[281] This provision prohibited the manufacture and importation of some firearms with certain features such as a folding stock, pistol grip, flash suppressor, and magazines holding more than ten rounds.
In the immediate aftermath of Hurricane Katrina, police and National Guard units in New Orleans confiscated firearms from private citizens in an attempt to prevent violence.
[295] When Lott's data was re-analyzed by some researchers, the only statistically significant effect of concealed-carry laws found was an increase in assaults,[295] with similar findings by Jens Ludwig.
[210] A 2004 National Academy of Sciences survey of existing literature found that the data available "are too weak to support unambiguous conclusions" about the impact of right-to-carry laws on rates of violent crime.
[298] A 2014 study found that Arizona's SB 1108, which allowed adults in the state to concealed carry without a permit and without passing a training course, was associated with an increase in gun-related fatalities.
[299] A 2018 study by Charles Manski and John V. Pepper found that the apparent effects of RTC laws on crime rates depend significantly on the assumptions made in the analysis.
[300] A 2019 study found no statistically significant association between the liberalization of state level firearm carry legislation over the last 30 years and the rates of homicides or other violent crime.
[312] Programs aimed at altering behavior range from passive (requiring no effort on the part of the individual) to active (supervising children, or placing a trigger lock on a gun).
[312] Many inherent challenges arise when working with children, including their tendency to perceive themselves as invulnerable to injury,[319] limited ability to apply lessons learned,[320][321] their innate curiosity,[320] and peer pressure.
[325] Dr. Hardy's study tracked the behavior of elementary age schoolchildren who spent a day learning the Eddie the Eagle four-step action plan from a uniformed police officer.
[337] The demonstration followed the Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School shooting in Parkland, Florida on February 14, 2018, which was described by several media outlets as a possible tipping point for gun control legislation.
The Federal government has spent over US$1.5 billion since the program's inception on the hiring of prosecutors, and providing assistance to state and local jurisdictions in support of training and community outreach efforts.
[359] In response to the spike in gun violence, a group of foundations and social service agencies created the Rapid Employment and Development Initiative (READI) Chicago.
[365] Additionally, the FBI states NIBRS will collect more detailed information, including incident date and time, whether reported offenses were attempted or completed, expanded victim types, relationships of victims to offenders and offenses, demographic details, location data, property descriptions, drug types and quantities, the offender's suspected use of drugs or alcohol, the involvement of gang activity, and whether a computer was used in the commission of the crime.
In statistical analysis of homicides and other types of crime which are rare events, these data tend to have poisson distributions, which also presents methodological challenges to researchers.
In 2013, after the December 2012 Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting, President Barack Obama ordered the CDC to resume funding research on gun violence and prevention, and put $10 million in the 2014 budget request for it.